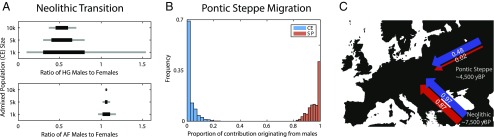
Fig. 3.
Estimated levels of sex bias during the Neolithic transition and Pontic Steppe migration. (A) Neolithic transition. The range of sex bias, measured as the ratio of males to females from a source population, that is consistent with the observed ratio of X and autosomal ancestries (Materials and Methods). Total contributions from the source population, the fraction of admixed individuals with a parent from that source population, are specified based on autosomal ancestry as 0.913 from AF and 0.087 from HG. Lines indicate that the observed ratios of X to autosomal ancestry in our dataset were present in the middle 50% (black) or middle 80% (gray) of 1,000 simulated admixed populations for specified CE population sizes. (B) Pontic Steppe migration. Under a model of constant admixture over time, the fraction of the total contribution of genetic material originating from males for each source population: CE and SP. Contributions are estimated from the migration parameter sets that have the smallest 0.1% Euclidean distance between observed and model-calculated ancestries. (C) Schematic of sex-specific migrations during the early Neolithic and later Neolithic/Bronze Age. Female contributions in are shown in red, and male contributions are shown in blue. Parameters are estimated under a single pulse migration model from Anatolia and under a constant migration model for the Pontic Steppe migration. The total contribution of each population is the average of female and male contributions from that source.