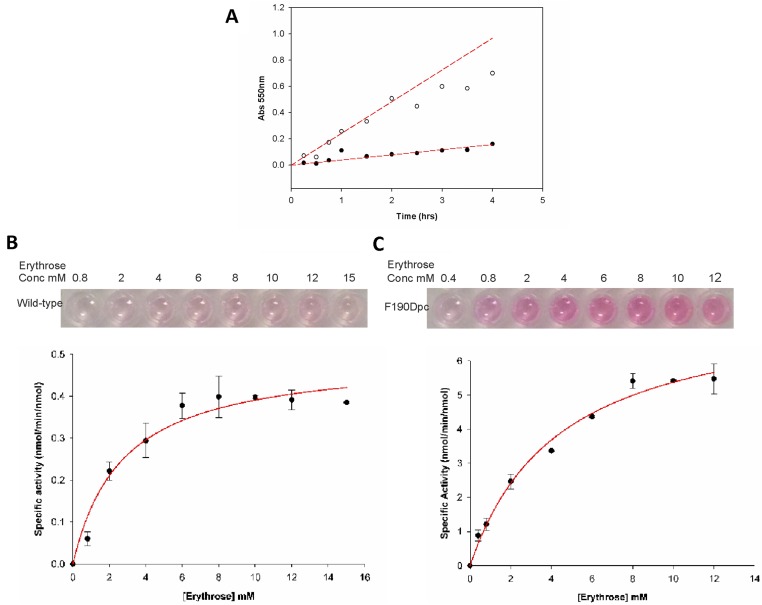
Fig. S4.
Wild-type and Phe190Dpc NAL kinetics with erythrose and pyruvate. Kinetic parameters were determined using the TBA assay. (A) Time course of the reaction. A 600-µL reaction containing 8.3 mM erythrose, 83 mM pyruvate, and 0.07 mg (2.1 nmol) enzyme was incubated for various times at room temperature. The 50-µL samples were taken from each reaction and stopped by the addition of 10 µL trichloroacetic acid (12% wt/vol). Precipitated proteins were removed by centrifugation and samples were analyzed by the TBA assay for the wild-type enzyme (•–•) or Phe190Dpc enzyme (○–○). The time course was shown to be linear over >90 min. (B) Wild-type and (C) Phe190Dpc: 100-µL reactions were set up with a range of erythrose concentrations (0.8–15 mM) and pyruvate (80 mM). Reactions were initiated by the addition of 25 µL of enzyme (0.7 mg/mL; 0.51 nmol). Samples were incubated at room temperature for 1.5 h. Activity was determined from the absorbance at 550 nm against a standard curve of N-acetylneuraminic acid. Samples were run in duplicate, and the average value was used to estimate kinetic parameters by fitting to the Michaelis–Menten equation using nonlinear regression analysis. Parameter values ± SE of the fit are reported.