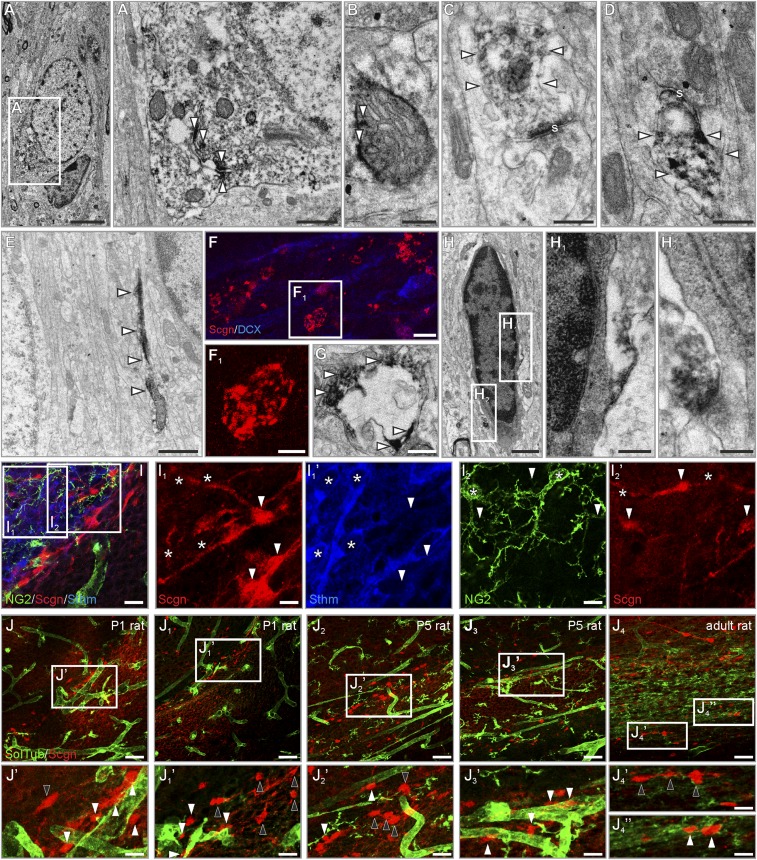
Fig. S1.
Presence and compartmentalization of secretagogin in rat RMS neurons. (A and B) Secretagogin was typically associated with intracellular membranes (open arrowheads in A1) in the cytoplasm or with mitochondria (open arrowheads in B). (C and D) In the neuropil, secretagogin was present in the postsynaptic compartment of immature synaptic-like structures (open arrowheads). (E) Secretagogin typically appeared in cellular processes. (F and G) Secretagogin+ round or oval pearl-like structures surrounded processes that probably were dendrites in the RMS. (H–H2) Dark, electron-dense glial cells remained immunonegative for secretagogin. (I–I2′) Secretagogin+ cells were invariably immunonegative for the glial marker NG2 (asterisks in I2 and I2′) and stathmin-2 (asterisks in I1 and I1′). (J–J4′′) Secretagogin+ neurons were randomly positioned with (white arrowheads) or without (black arrowheads) a close association with vessels in P1, P5, and adult rats. s, synapse; SolTub, Solanum Tuberosum agglutinin. (Scale bars: 50 m in J–J4; 10 µm in I–I2′ and J1′– J4′′; 3 µm in F; 2 µm in A; 1 µm in E; 300 nm in A1, B–D, F1, G, and H; and 200 nm in H1 and H2.)