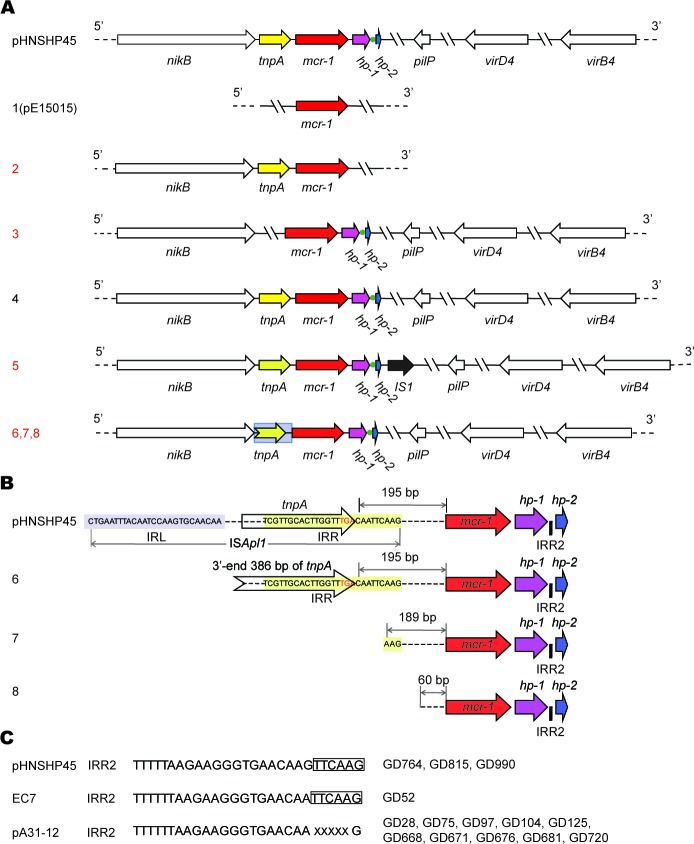
Figure 2. Genetic diversity in the mcr-1-harbouring plasmids from the swine gut microbiota.
A. Scheme of the eight types of the mcr-1-harbouring plasmids. The plasmid pHNSHP45 is a prototype with known genome sequence [8], whereas the other eight types of plasmids are revealed after PCR-based sequencing of the 89 representative mcr-1-containing plasmids collected from three pig farms in Guangdong province of China, in 2016. Arrows denote the known (and/or putative) genes/loci. The mcr-1 gene is highlighted in red and 100% identical. The broken arrow marked in grey background denotes the partial sequence of tnpA gene at its 3′-end. The tnpA locus is PCR-negative in type 1 and 3. The green dot represents the IRR2 site. Apart from the type 1 and 2, all the other six types (3-8) are PCR-positive for the four genes (nikB, pilP, virD4 and virB4), as well as a hypothetical protein (hp), adjacent to the 3′-end of mcr-1. Unlike the other types with an intact tnpA adjacent to the 5′-end of mcr-1, types 6, 7 and 8 feature with the truncated versions of tnpA. In type 1 like pE15015 we recently reported, only the mcr-1 locus is PCR-positive. In type 2, two more loci (nikB and tnpA) can be detected in the PCR assays. In particular, an extra-insert IS1 transposase with 97% identity to the counterpart of Acinetobacter baumannii by BlastX (illustrated with a dark arrow) is closely present at the 3-end of hp in the type 5 of plasmid. In addition to the two known types (1 and 4) we reported very recently [9], we show six new plasmid types (2, 3, 5, 6, 7 and 8 labeled in red) in this study. B. Molecular insights into truncated versions of the mcr-1-containing ISApl1 mobile element. In the new plasmid types 6, 7 and 8, the tnpA transposase gene is variously featuring with truncated versions. Designations: IRL, Inverted Region Left; IRR, Inverted Region Right. C. Sequence feature of the IRR2 site. X denotes the variable nucleotide.