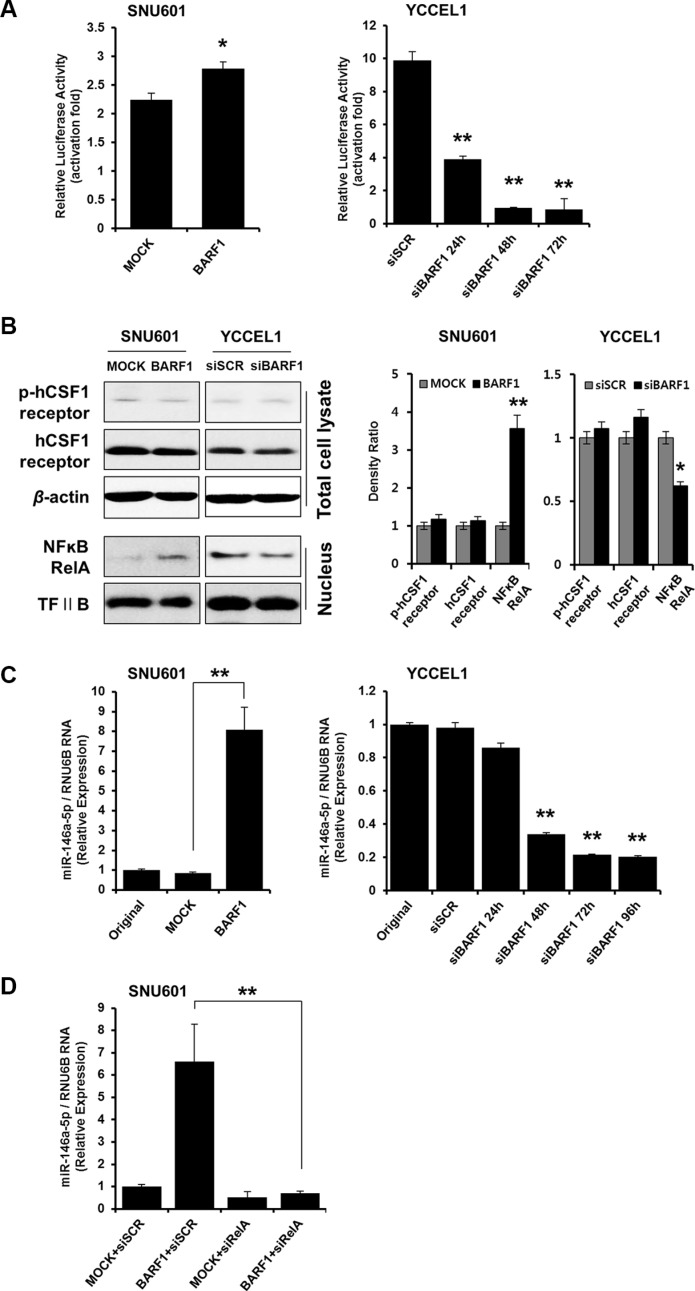
Figure 2. BARF1 upregulated miR-146a-5p in an NFκB-dependent manner.
(A) Cells were transfected with an NFκB-dependent luciferase reporter together with Renilla luciferase. After 72 h, NFκB activity was determined using a dual-luciferase assay. SNU610 BARF1 cells demonstrated higher NFκB transcriptional activity than SNU601 mock cells (*P < 0.05). YCCEL1 cells transfected with 20 nM BARF1-specific siRNA (siBARF1) showed lower NFκB transcriptional activity than YCCEL1 cells transfected with scrambled siRNA (siSCR) (**P < 0.01). (B) Phospho-hCSF1 receptor and hCSF1 receptor showed similar levels irrespective of BARF1 presence or knockdown, whereas NFκB RelA and miR-146a-5p increased in response to BARF1. (C) TaqMan quantitative real-time RT-PCR showed higher miR-146a-5p levels in SNU601 BARF1 cells than in SNU601 mock cells or untransfected SNU601 cells (**P < 0.01). Conversely, miR-146a-5p expression was markedly decreased in YCCEL1 cells transfected with BARF1-specific siRNA (siBARF1) compared with YCCEL1 cells transfected with scrambled siRNA (siSCR) or untransfected YCCEL1 cells (**P < 0.01). (D) SNU601 BARF1 cells were transfected with 20 nM NFκB RelA-specific siRNA (siRelA) or scrambled siRNA (siSCR). BARF1-induced miR-146a-5p upregulation was neutralized by NFκB RelA inhibition (**P < 0.01). All experiments were performed in triplicate.