Figure 7. Liver protection mechanism of plumbagin.
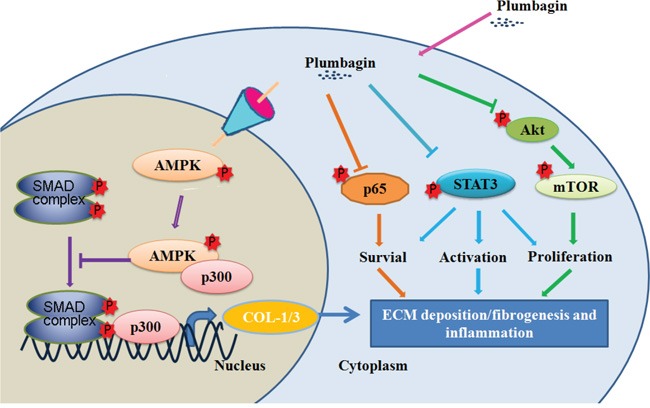
Plumbagin increased AMPK phosphorylation that promoted AMPK binding to p300, which is a SMAD transcriptional cofactor. This may further competitively decreases the p300/SMAD complex initiated transcription for COL-1/3 and α-SMA. Plumbagin also attenuated NF-κB, STAT3, and Akt/mTOR signals in LX-2 cells, which were involved in pro-inflammation and survival of HSCs/myofibroblasts. In conclusion, these findings indicate that plumbagin may be a powerful drug candidate to protect the liver from acute and chronic damage by inhibiting inflammation and collagen production.
