Figure 2. A flowchart for the identification of independent prognostic factors in patients with DLBCL.
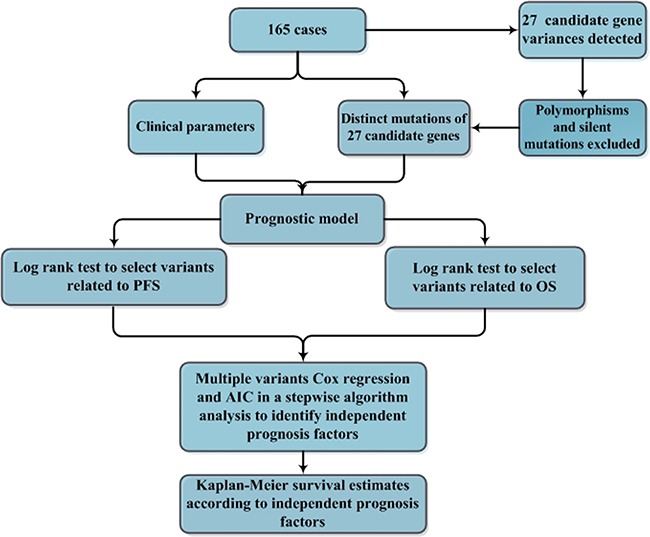
A total of 165 cases of DLBCL, NOS were included in the analysis for identifying independent prognostic factors in patients with DLBCL. Polymorphisms and silent mutations of 27 gene variations detected by next generation sequencing in the DLBCL cases were excluded, and distinct mutations were confirmed by Sanger sequencing. To indentify the prognostic factors, the mutation status of the 27 genes and clinical features, including age, gender, B symptoms, massive mass, Ann Arbor stage, extranodal involvement, bone marrow involvement, ECOG, elevated LDH, MYC aberration (including translocation and amplification) were selected as candidate parameters. The selected parameters were initially analyzed by the log-rank test to identify potential univariate prognostic factors related to PFS or OS. The resulting parameters were further analyzed in a multivariate modeling by multiple variable Cox regression and the generalized Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) to identify the independent prognostic factors. The independent prognostic factors were finally analyzed by log-rank tests to distinguish the significant difference of their roles in PFS or OS estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method.
