Figure 4.
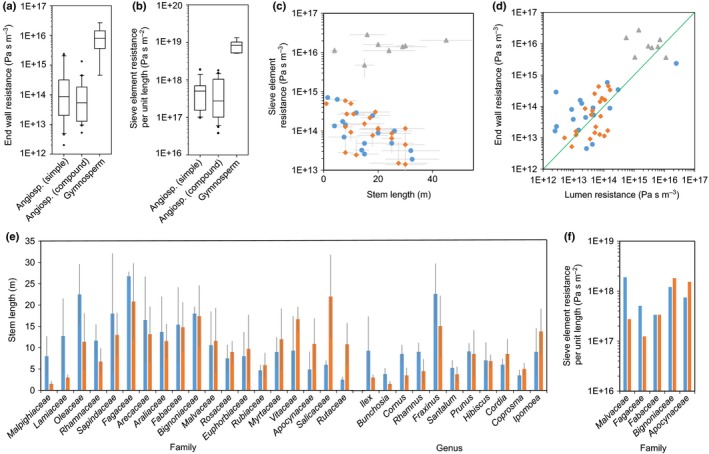
Relationship between sieve element end wall type and hydraulic resistance. (a, b) Box plots of end wall resistance calculated according to Eqn 1 (a), and sieve element resistance per unit length calculated according to Eqn 2 (b) show similar average values for angiosperms species with simple end walls and angiosperms with compound end walls, but higher values for gymnosperms. (c) Differences between the angiosperms and gymnosperms (gray triangles) are visible for sieve element resistance per unit length over the whole range of stem lengths, but not between angiosperms with simple (blue circles) and compound end walls (orange diamonds). (d) The relationship of sieve element lumen to end wall resistance was found to be close to a 1 : 1 ratio (green line) for all plants. (e, f) Closely related angiosperm species with different end wall type show no relationship between end wall type and stem length (e) or sieve element resistance per unit length (f). Blue bars, simple end walls; orange bars, compound end walls. Error bars indicate ± SD.
