Figure 2.
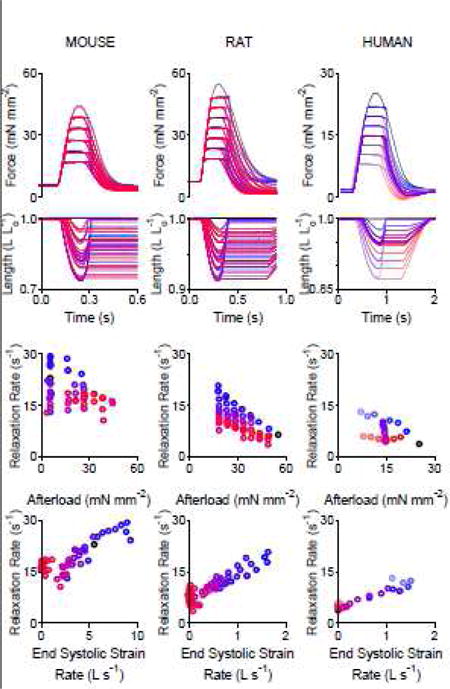
Relaxation rate is dependent on the end systolic strain rate in mouse, rat, and human myocardial trabeculae. Top: Force and length versus time traces. Bottom: Relationship between relaxation rate and end systolic strain rate. Each column shows multiple afterload-clamped twitches overlaid from a single mouse trabecula (53 twitches), rat trabecula (62 twitches), and human (25 twitches) trabecula. Six additional rat trabeculae shown in Supplementary Figure S2.
