Figure 5.
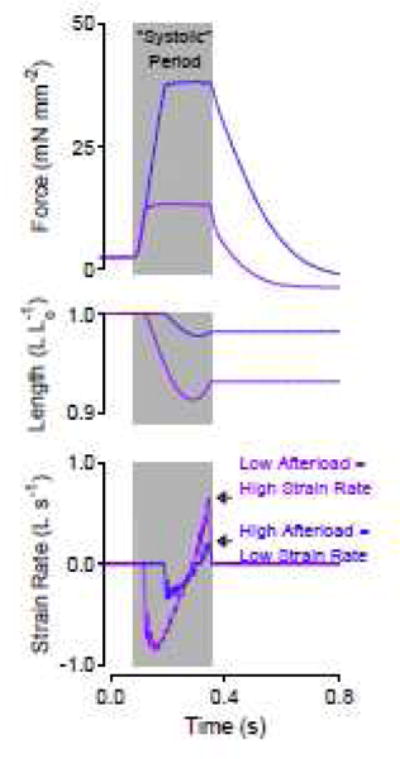
A short, quick relengthening explains why relaxation rate can be faster at reduced afterloads. Force, length, and strain rate versus time for two twitches load-clamped at different afterloads but allowed to relengthen for equal durations. Afterload may have been mistaken for the mechanical factor that modified relaxation rate in intact hearts because strain and strain rate were not measured.
