Figure 7.
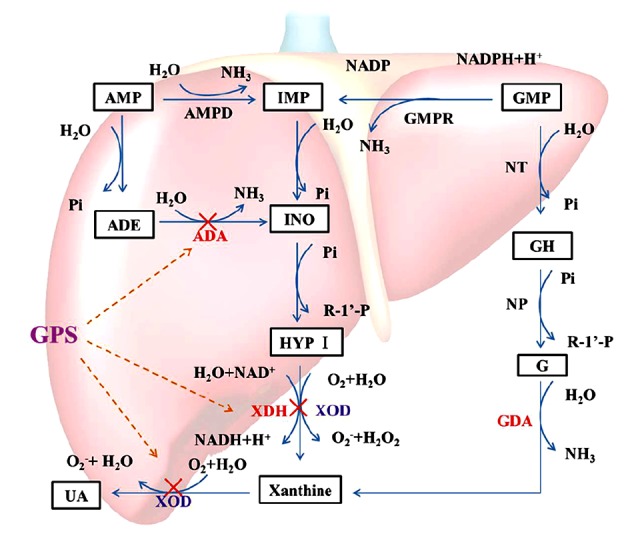
Catabolism of purine nucleotides. Xanthine oxidoreductose (XOR) catazyles the oxidation of hypoxanthine and the oxidation of xanthine to uric acid, by utilizing either NAD+ or O2. As a results of these reactions, superoxide anion (O2−) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), are produced. XDH prefers NAD+ as the susbtrate and XOD prefers O2. Uric acid is the final oxidation product of purine (adenine and guanine) metabolism in humans and higher primates. The anti-hyperuricemia effect of GPS may be related to a decrease in Xanthine Oxidoreductase through the XOD/XDH system. “×”– inhibit.
