Figure 8.
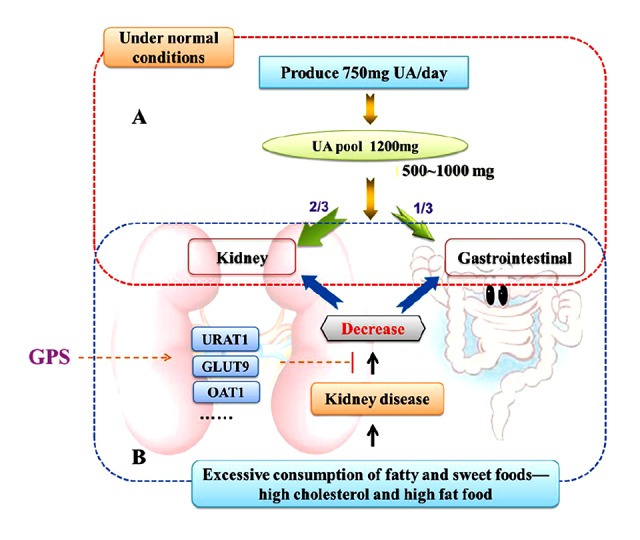
Uric acid removal. (A) Under normal conditions, UA is the end product of purine metabolism in humans and higher primates, the average uric acid pool in the normal human body is 1200 mg, every day produce UA is about 750 mg and excrete about 500~1000 mg. About 70% of the daily turnover of uric acid humans is excreted by the kidneys, while the other 30% enters the intestine where it is further broken down by colonic bacteria and eliminated. (B) Excessive consumption of fatty and sweet foods, like high cholesterol and high fat food affect the kidney functions, and the absorption of uric acid in the proximal tubule increased or (and) secretion function decreased by renal tubular dysfunction, the serum level of uric acid will increase and hyperuricemia will occur. GPS possibly has the uricosuric activity mediated by the regulation of renal mURAT1, mGLUT9 and mOAT1 in hyperuricemic rats.
