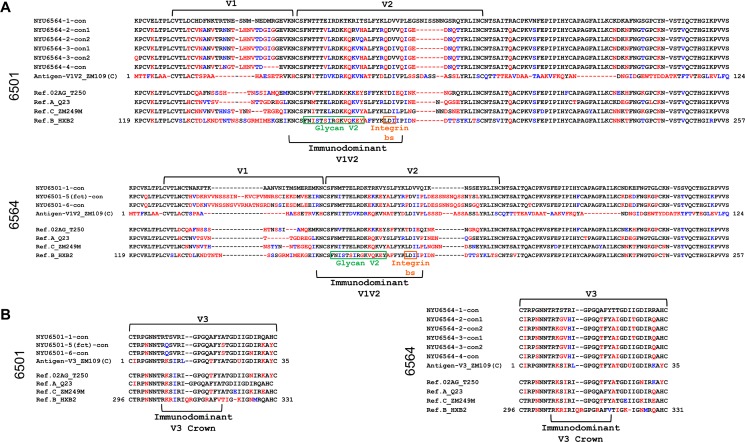
Fig 5. Multiple amino acid alignments of V1V2 and V3 regions with NYU6501 and NYU6564 envelope consensus sequences pre and post superinfection.
Alignments were made with consensus sequences generated from all functional Env clones per time point of NYU6501 and NYU6564 (according to phylogenetic analyses in Fig 2); two consensus sequences per time point were created when distinct populations were detected (Fig 2; see S2 Fig). Patient Env sequences were aligned with V1V2 and V3 antigens (≥10 fold change in EC50, Fig 4B; S2 Table) and reference strains of subtypes CRF02_AG, A, C and B, also used as pseudoviruses for neutralization. Red residues indicate a nonsynonymous substitution and blue residues indicate isofunctional mutations compared to the time point 1 consensus sequence before SI, thereby indicating changes post-SI. A) Patient V1V2 consensus sequences aligned with the V1V2 ZM109 antigen used for binding experiments and reference sequences. Green and yellow boxes indicate the residues that make up the glycan V2 region and the integrin binding site, respectively, located within the immunodominant V1V2 region. V1 and V2 loops are indicated with brackets. B) Patient V3 sequences compared with the V3 ZM109 antigen and reference sequences. The V3 crown residues are denoted underneath.