Figure 1.
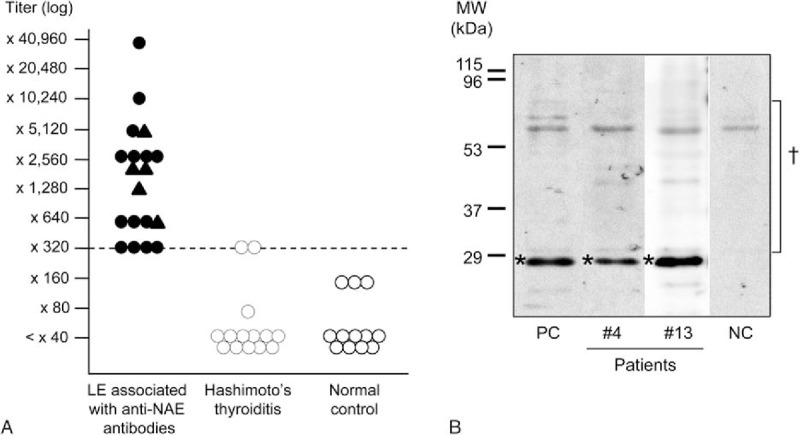
Titer distributions and immunoblotting of anti-NH2-terminal of α-enolase (NAE) antibodies. A, Anti-NAE antibody titers of patients with LE associated with anti-NAE antibodies, patients with Hashimoto thyroiditis, and normal controls. The cut-off level for positivity is indicated by the dashed line (titer: ×320). In patients with LE associated with anti-NAE antibodies, triangles indicate patients with antibodies to both NAE and other antigens (i.e., the voltage-gated potassium channel (VGKC) complex); circles indicate patients who are positive only for anti-NAE antibodies. B, Representative findings of immunoblotting of a recombinant amino NAE with serum from patients with limbic encephalitis (LE) associated with anti-NAE antibodies. An NAE signal was detected around 29 kDa for the sera of Cases 4 and 13. ∗Position of the recombinant NAE; †Derivatives of human cells that were cultured for NAE expression and showed nonspecific reactions with sera; NC = negative control, PC = positive control.
