Figure 5. In vitro technetium-99m-ethylenedicysteine-N-acetylglucosamine (99mTc-ECG) uptake in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cells and in vivo 99mTc-ECG imaging in a severe combined immunodeficiency mouse lymphoma model.
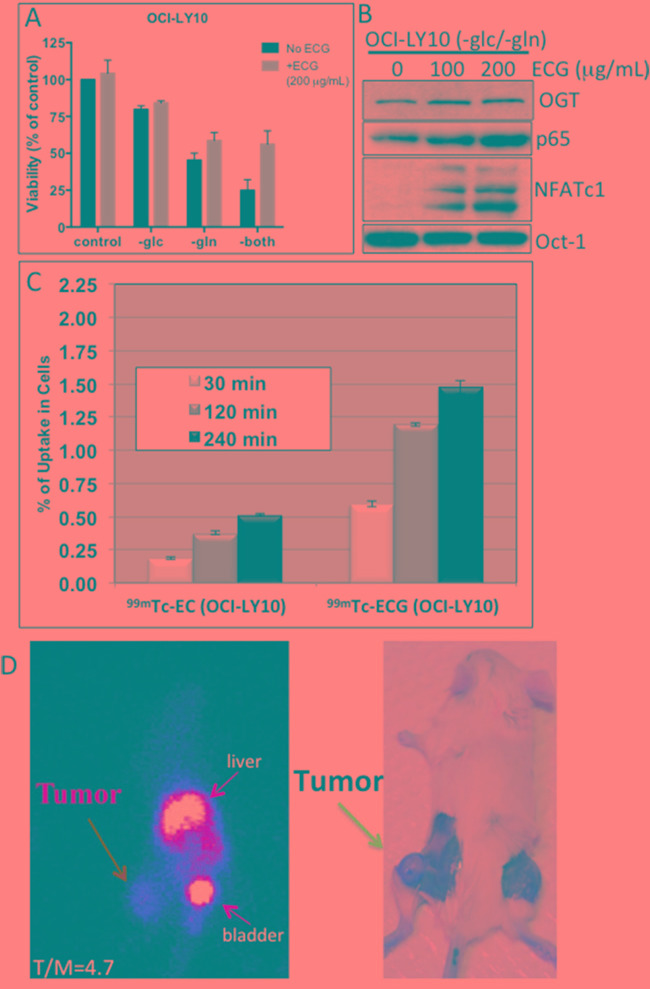
A. OCI-LY10 cells were cultured without glucose (-glc), glutamine (-gln) or both (-both) and supplemented with ECG (+ECG; 200 μg/ml) or without ECG (No ECG). Viability was assessed after 48 h of incubation. B. OCI-LY10 cells were cultured without glucose and glutamine and were supplemented with various doses of ECG. After 48 h, purified nuclear extracts were subjected to Western blot analysis for O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase (OGT), nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB)-p65, nuclear factor of activated T-cells 1 (NFATc1), and Oct-1 (loading control). C. In vitro uptake of 99mTc-ECGin a representative DLBCL cell line (OCI-LY10). D. Planar scintigraphy 99mTc-ECG image (left panel) shows a hightumor-to-muscle (T/M) ratio at 120 min (left panel), and a necropsy image of the same mouse shows the tumor on the left thigh (right panel)
