Figure 3. miR-22 inhibits migration and invasion of HCC cells through directly targeting YWHAZ expression.
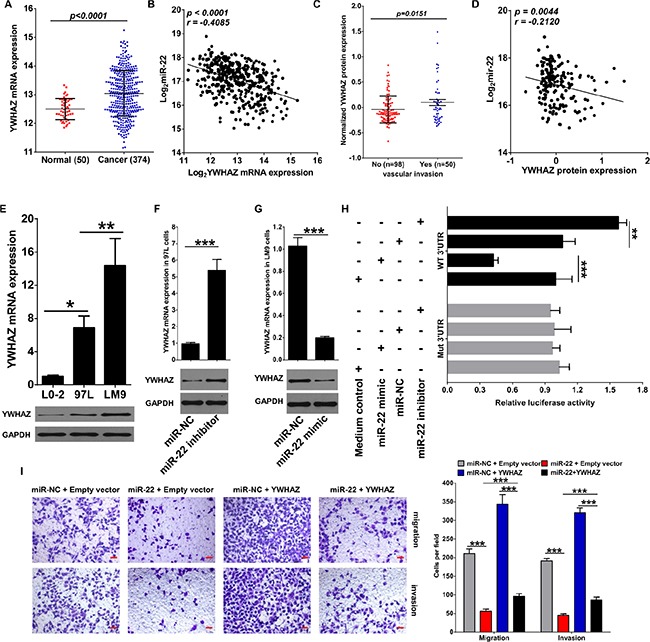
(A) mRNA expression of YWHAZ in tumor tissues and adjacent normal tissues of HCC patients was revealed by mRNA-seq provided by TCGA. (B) Scatterplot depicts a significant inverse correlation between miR-22 and YWHAZ mRNA expression. (C) Normalized protein expression of YWHAZ in HCC patients with or without vascular invasion revealed by Reverse Phase Protein Array (RPPA) analysis. (D) Scatterplot depicts a significant inverse correlation between miR-22 and YWHAZ protein expression. (E) YWHAZ expression in normal liver cell line L0-2 and HCC cell lines MHCC97L and HCCLM9 was determined by qRT-PCR and western blotting. GAPDH was used as an internal control. (F) Effect of miR-22 inhibitor on YWHAZ expression was determined in MHCC97L cells. (G) Effect of miR-22 mimic on YWHAZ expression was determined in HCCLM9 cells. (H) miR-22 mimic significantly suppressed luciferase activity of YWHAZ containing a wild-type 3′-UTR, but showed no effect on activity of YWHAZ with a mutant 3′-UTR, whereas treatment with miR-22 inhibitor increased luciferase activity of YWHAZ. (I) Overexpression of YWHAZ partially rescued the inhibitory effects of miR-22 on migration and invasion of HCC cells. Scale bar represents 50 μm. Data are displayed as the Mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.0001. (miR-NC: miR-22 negative control, WT: wild type; Mut: mutant type).
