Figure 7. Effect of celecoxib, dimethyl-celecoxib, or the COX1/COX2 inhibitor indomethacin on colony formation of Ph+ CML cells and normal CD34+ progenitors.
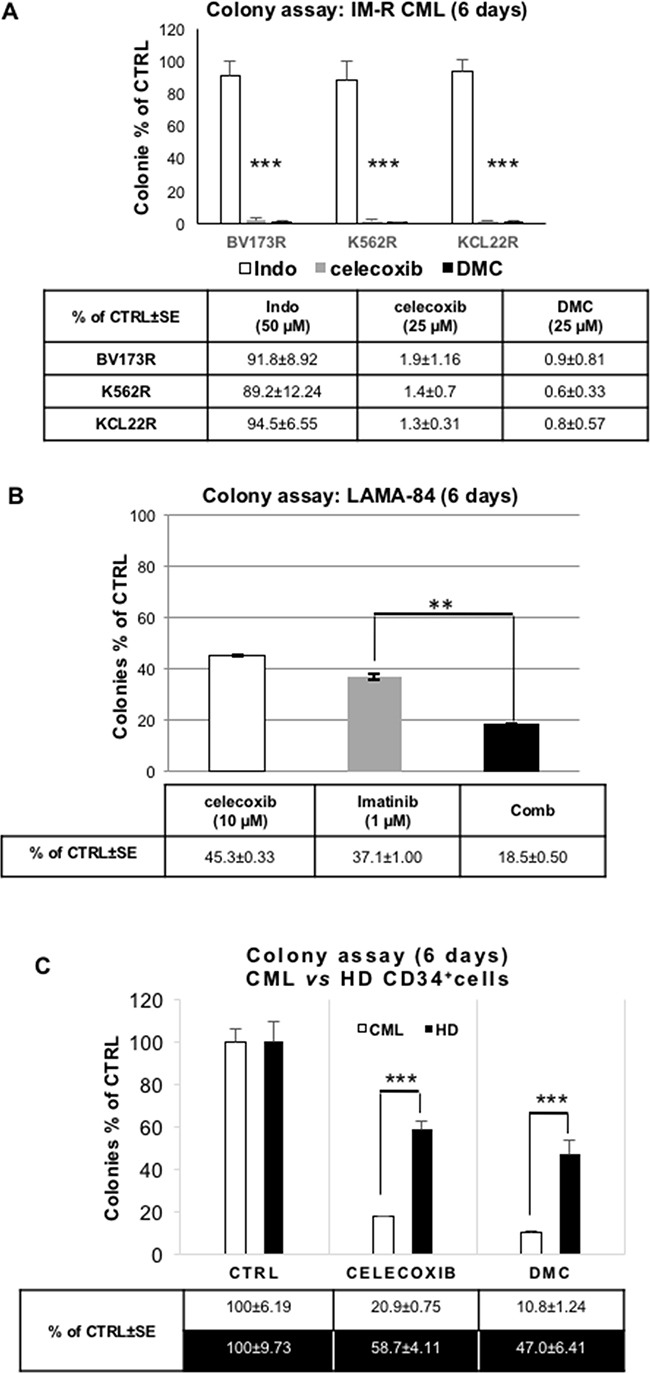
A. Colony assay of imatinib-resistant (IM-R) CML blasts (cell lines: BV173R, K562R, KCL22R) treated with celecoxib (25 μM) or dimethyl-celecoxib (25 μM; DMC). Indomethacin (Indo; 50 μM), a COX1 and COX2 inhibitor, was included as a control. Values are the means of three independent experiments made in duplicate ± S.E.M. ***P ≤ 0.001. B. Colony assay of LAMA-84 cells treated with celecoxib (10 μM) and/or imatinib (1 μM). Values are the means of three independent experiments in duplicate ± S.E.M. **P ≤ 0.01. C. Colony assay of celecoxib or dimethyl-celecoxib (DMC) treated CD34+ CML cells (mean of 4 different samples) or normal cord blood-derived CD34+ cells from healthy donors (HD; mean of 4 different samples). Cells were treated with 25 μM of either drug before seeding (10,000 cells/plate) onto 80% methylcellulose in the presence of a cytokine cocktail. Colonies were scored after 9 days; ***P ≤ 0. 001.
