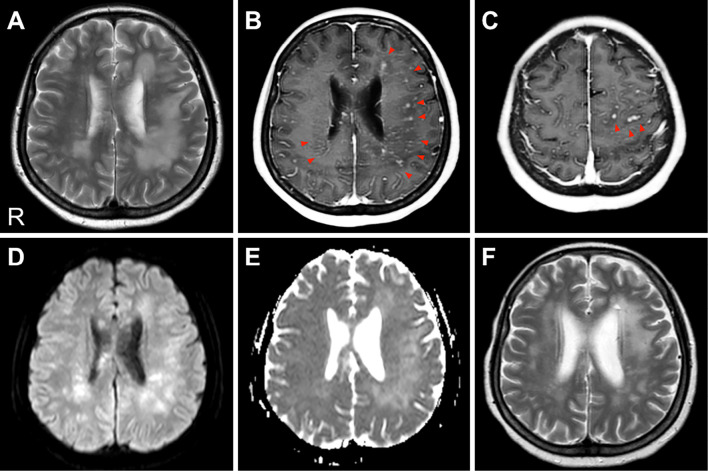
Figure 1.
Cranial MRI. (A) A T2-weighted image (TR/TE=3,000.0/80.0 ms). High-intensity plaque lesions are evident in the bilateral cerebral white matter, predominantly on the left side. (B, C) A gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted image (TR/TE=6.0/2.3 ms). These lesions are enhanced with gadolinium, especially in the perivascular sites (red arrows). No gadolinium enhancement of the meninges was detected. (D, E) A diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and an apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map (b=1,000 s/mm2, TR/TE=5,000.0/65.0 ms). Both DWI and the ADC map show increased values in the involved areas. (F) A T2-weighted image (TR/TE=3,000.0/100.0 ms) after steroid pulse therapy. The high-intensity lesions of the white matter were significantly reduced. R: right