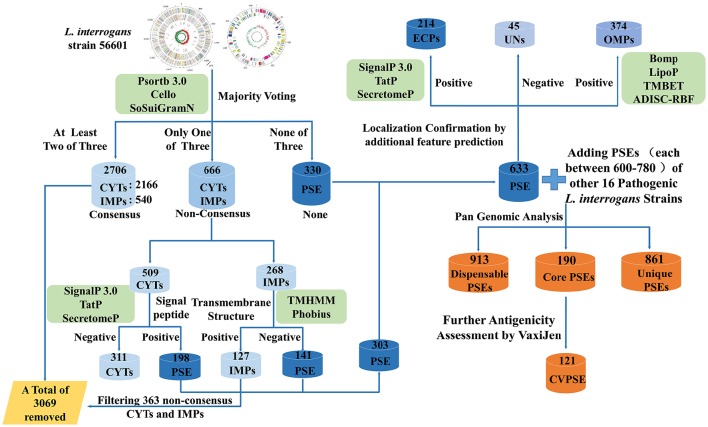
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the novel strategy of reverse vaccinology applied to Pathogenic L.interrogans. In Figure 1, L. interrogans str.56601 was selected as a representative example for elucidating the step-by-step process and predicted results of PSEs using the novel RV negative strategy. Similarly, PSEs of the other 16 representative strains of pathogenic L. interrogans were predicted following same strategy as str.56601. First of all, PSORTb3.0, CELLO, and SOSUI-GramN were used to predict subcellular localization of these proteins by majority voting strategy. Proteins predicted as CYTs and IMPs by at least two of the three bioinformatic tools were defined as consensus CYTs and IMPs and were directly removed from further study. Proteins predicted as CYTs or IMPs by only one of the three tools were labeled as non-consensus CYTs or IMPs, respectively. The remaining proteins were labeled as PSEs. Then, both the non-consensus CYTs with no signal peptides predicted by all of SignalP3.0, TatP and SecretomeP and the non-consensus IMPs with positive transmembrane structures predicted by TMHMM or Phobius were defined as Non-PSEs and removed from further study, whereas the remaining non-consensus CYTs with positive signal peptide and non-consensus IMPs with no transmembrane structure were added into the predicted PSEs. In addition, SignalP3.0, Tat and SecretomeP as well as BOMP, TMBETADISC-RBF, and LipoP were utilized to further investigate extracellular features of these PSEs. Finally, pan-genome analysis of the predicted PSEs among the 17 pathogenic L. interrogans strains identified the core, dispensable, and unique PSEs. And the core PSEs with high antigenicity values predicted by the VaxiJen server were determined as final vaccine antigen candidates. PSE, potential surface-exposed proteins; CVPSE, Conserved Vaxijen antigenicity predicted PSE.