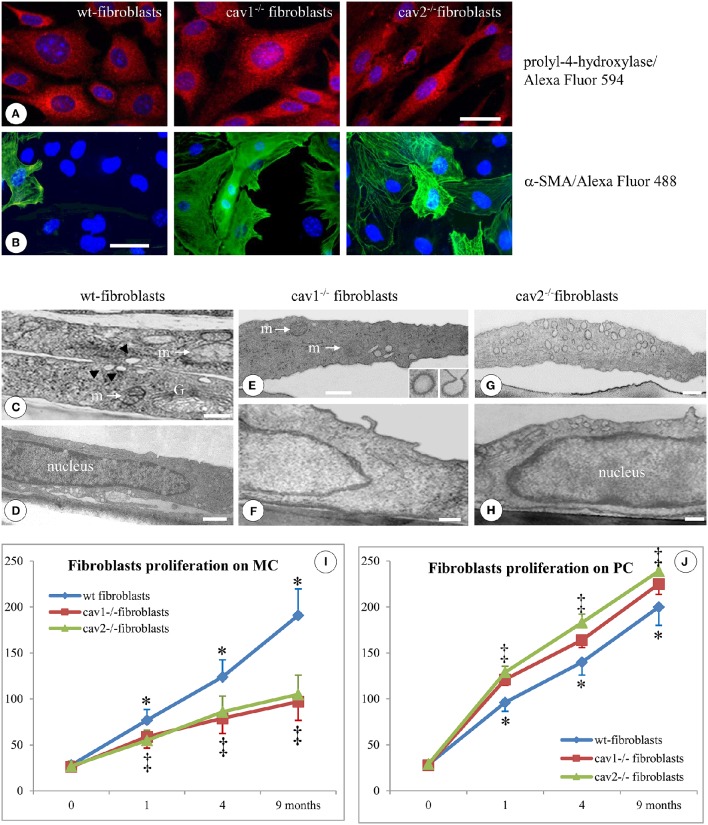
Figure 1.
Specific morphological and proliferative features of isolated mouse lung fibroblasts. Immunofluorescent staining of fibroblasts isolated from 2 months old mice (1 day after confluence) for the prolyl-4-hydroxilase specific marker reveals its presence in all three types of cells; n = 7. (B) Staining of isolated fibroblasts (same conditions as in A) with α-SMA Ab showing a higher number of positive cells in Cav1−/− and Cav2−/− phenotype; n = 8. Bars: 30 μm (A); 25 μm (B). EM morphology of isolated fibroblasts illustrates by sections through the cells outside the nuclear area (C,E,G) and sections through the nuclear area (D,F,H). (C) Two overlapping wt-fibroblasts display most of regular organelles: Golgi -G-, mitochondria –m-, caveolae (arrows); (D) and a nucleus with an continuous rim of condensed chromatin; n = 6. (E,F) Cav1−/− fibroblasts show total lack of caveolae, while they do have CCVs (insets) all other subcellular organelles, including mitochondria (m), ER spread throughout the cytosol and the nucleus is filled with relaxed chromatin; n = 6. (G) The Cav2−/− fibroblasts showing a sizable population of caveolae identical in size, number and cellular distribution with wt-fibroblasts, along with a nucleus crammed with relaxed chromatin (H). Bars: 150 nm (C); 200 nm (D,F); 350 nm (E); 300 nm (G,H). (I) When isolated fibroblasts were seeded on monomeric collagen-1 (MC) the wt-fibroblasts (blue graph) display a 50% increase in their proliferation vs. Cav1−/− fibroblasts (red graph) and Cav2−/− fibroblasts (green graph). (J) Cav-null fibroblasts isolated from the lungs of mice at different ages when plated in polymeric collagen-1 (PC) are more proliferative (>20%) than the corresponding wt-fibroblasts; 0 means 2 weeks of age, while 1, 4, and 9 are months (m) after birth. n = 12; *p < 0.05 and ‡p < 0.01 between different months. In all conditions (MC and PC) the differences between 1, 4, 9 months, and 2 weeks are statistically significant p < 0.01. Note also the lack of statistical differences between cav1−/− and cav2 −/− null fibroblasts in both experimental conditions as well as at different time points.