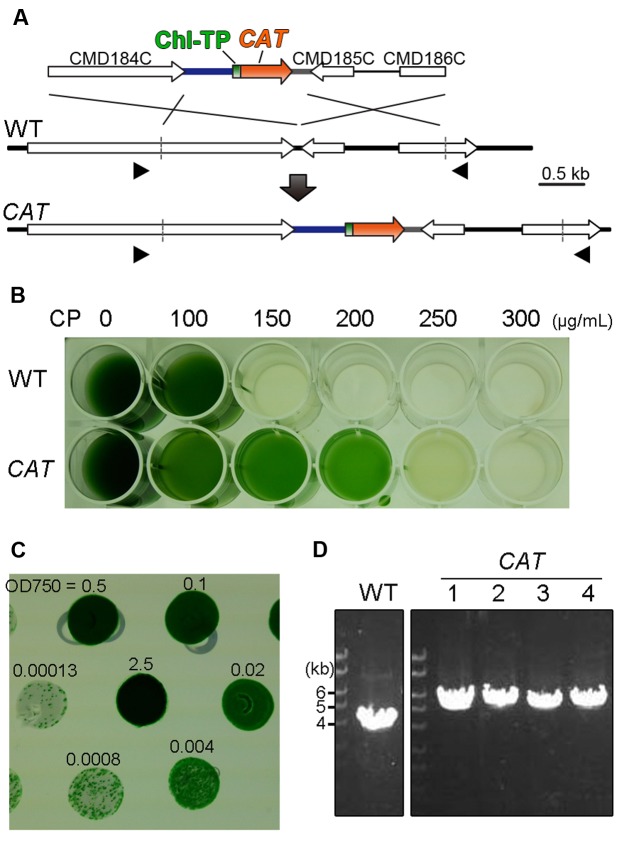
FIGURE 1.
Development of the selection system using chloramphenicol and the CAT selection marker. (A) Schematic diagram of CAT gene insertion into the intergenic region between CMD184C and CMD185C by homologous recombination. The first line indicates the introduced liner DNA vector and the second line indicates the genomic structure of the parental wild-type (WT) strain. For the efficient expression of CAT (orange) and the translocation of the CAT protein into the chloroplast, the 600-bp upstream flanking sequence of the APCC orf, the sequence encoding the chloroplast-transit peptide (Chl TP) of APCC and the 200-bp downstream flanking sequence of the β-tubulin orf were utilized as the promoter (blue), the chloroplast-transit peptide (green) and the polyadenylation signal sequence (gray), respectively. The third line indicates the expected genomic structure of the CAT strain. The arrowheads indicate the positions of the PCR primers No. 43 and No. 44 used in (D). The exact positions and sequences are indicated in Supplementary Table S1. (B) The selection of CP-resistant transformants in the liquid medium supplemented with a series of concentrations of CP. (C) Single-colony isolation of transformed cells on the solidified (gellan gum) medium without CP. Transformed cells, which were selected in the liquid medium supplemented with CP, were washed with CP-free medium. Then cells were serially diluted as indicated and spotted on the plate. (D) PCR analysis of the independent CAT transformants was performed to confirm the homologous recombination event. The WT strain was used as a negative control. The positions of PCR primers No. 43 and No. 44 are shown in (A) and the exact positions and sequences are indicated in Supplementary Table S1. The predicted size of the PCR product is 5.4 kb for CAT-targeted insertion and 3.8 kb for CAT-off-targeted insertion, respectively.