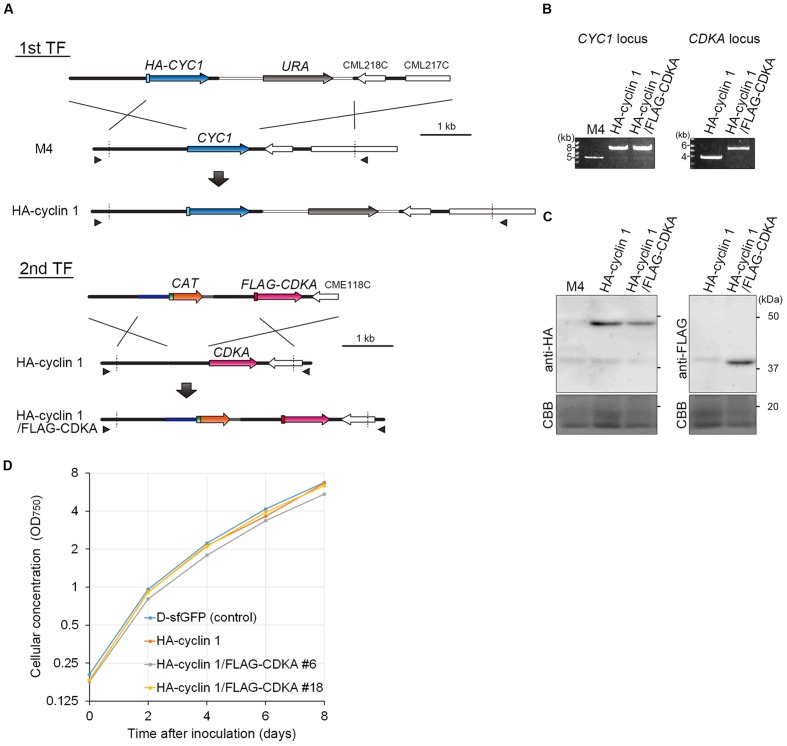
FIGURE 3.
Production of the HA-cyclin 1 and FLAG-CDKA expressing double-knock-in strain. (A) Schematic diagram of the knock-in of HA-CYC1 and FLAG-CDKA into the chromosomal CYC1 and CDKA loci by homologous recombination. The first line indicates the linear DNA vector that was transformed into the M4 strain. The second and third lines indicate the genomic structure of the parental M4 strain and resultant HA-cyclin 1 strain, respectively. The fourth line indicates the linear DNA vector that was transformed into the HA-cyclin 1 strain. The fifth and sixth lines indicate the CDKA locus of the parental HA-cyclin 1 strain and the resultant HA-cyclin 1/FLAG-CDKA strain, respectively. The arrowheads indicate the positions of the PCR primers used in (B). (B) PCR analysis of the HA-cyclin 1 and the HA-cyclin 1/FLAG-CDKA strains, confirming the occurrence of homologous recombination events. The M4 strain was used as a negative control. The positions of the primer sets No. 45/No. 46 and No. 47/No. 48 are shown in (A) and the exact positions and sequences are indicated in Supplementary Table S1. The predicted size of the PCR product amplified from the CYC1 locus is 6.8 kb for the HA-cyclin 1 strain and 4.0 kb for the M4 strain. The predicted size of the PCR product amplified from the CDKA locus is 4.5 kb for the HA-cyclin 1/FLAG-CDKA strain and 2.9 kb for the HA-cyclin 1 strain. (C) Immunoblotting with the anti-HA and the anti-FLAG antibodies. The predicted sizes of HA-cyclin 1 and FLAG-CDKA proteins are 48 and 40 kDa, respectively. (D) Growth curves of the D-sfGFP strain (an sfGFP expresser was used as a control), the HA-cyclin 1 and the HA-cyclin 1/FLAG-CDKA strains.