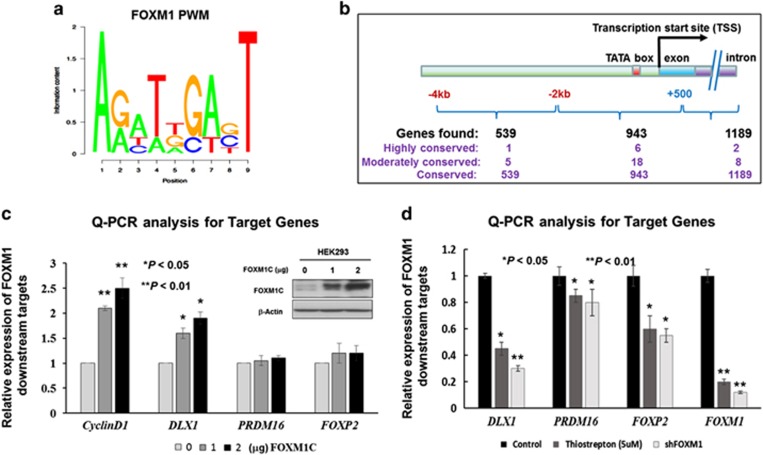
Figure 1.
Prediction of the putative downstream targets of FOXM1 by PWMSCAN. (a) PWM for FOXM1-binding motif sequence. (b) A schematic diagram summarizing the computational predictions of the putative targets of FOXM1, which are divided into three groups based on the positions of the FOXM1-binding sites. The genes are further classified into three subgroups according to degree of human–mouse conservation of their putative binding sites. (c) Western blot and qRT-PCR analyses showed concentration-dependent increases in DLX1, PRDM16 and FOXP2 expression following transient transfection of a FOXM1 expression plasmid. The expression of CyclinD1 was used as a positive control for FOXM1 expression. Both β-actin and GAPDH were used as internal controls. (d) The qRT-PCR analysis showed that the inhibition of FOXM1 by treatment with Thiostrepton inhibitor (5 μm, 24 h) or shRNAi-mediated FOXM1 knockdown was accompanied by a remarkable reduction of the three putative targets, DLX1, PRDM16 and FOXP2, compared with their respective untreated or scrambled controls of A2780cp (*P<0.01 and **P<0.05, Student's t-test).