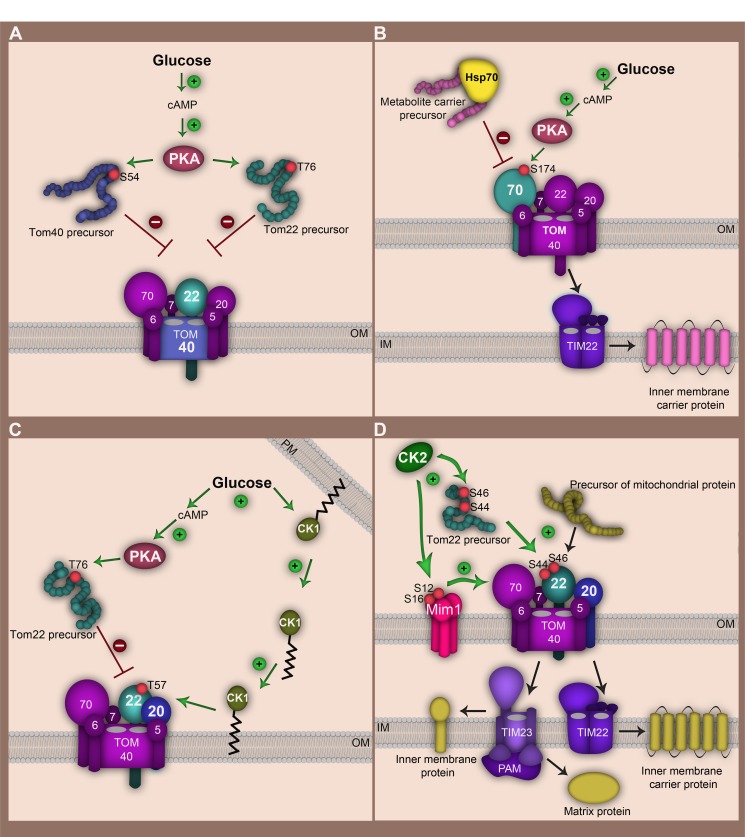
Figure 2. FIGURE 2: Regulation of the TOM complex by cytosolic and outer membrane bound kinases in the yeast S. cerevisiae.
(A) Glucose induces an increase in cAMP synthesis and PKA activation. PKA phosphorylates Tom40 and Tom22 precursors in the cytosol at serine 54 and threonine 76, respectively. Translocation of phosphorylated precursors to the outer membrane and their assembly into the mature TOM complex is thereby impaired.
(B) Glucose-driven activation of PKA inhibits import of metabolite carrier precursors. PKA phosphorylates the Tom70 receptor at serine 174. This modification impairs interaction of Tom70 with the metabolite carrier/chaperone complex.
(C) Glucose signalling leads to retranslocation of CK1 from the plasma membrane (PM) to the mitochondrial outer membrane. CK1 targets threonine 57 at Tom22 promoting Tom22 assembly (by enhancing its interaction with Tom20). CK1 acts downstream of PKA thereby mitigating strong PKA activity.
(D) CK2 exerts a stimulatory role on TOM complex biogenesis and activity. Phosphorylation of Tom22 precursor at serine 44 and serine 46 facilitates its interaction with Tom20 receptor and stimulates assembly of Tom20 into the TOM complex. In addition CK2 modifies serine 16 and serine 14 of Mim1 enhancing its stability and promoting Mim1-dependent import of Tom20 and Tom70 precursors. CK2 regulation of the TOM-complex thereby influences downstream import pathways. OM, mitochondrial outer membrane; IM, mitochondrial inner membrane.