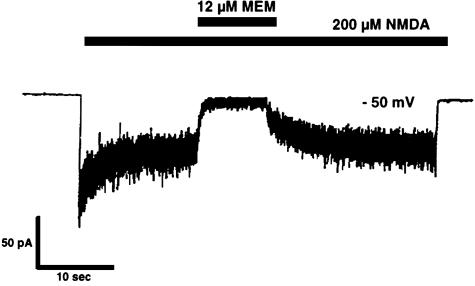
FIG. 4.
Blockade of NMDA current by memantine. At a holding potential of approximately −50 mV, whole-cell recording of NMDA-evoked current from a solitary neuron revealed that the on-time (time until peak blockade) of micromolar memantine was approximately 1 second, while the off-time (recovery time) from the effect was ∼5.5 seconds. The application of memantine produced an effective blockade only during NMDA receptor activation, consistent with the notion that its mechanism of action is open-channel block.10