Figure 1. FIGURE 1: Intracellular ROS accumulation, ATP release and activation of caspase like activity in C. parapsilosis (MICA-S and MICA-NS isolates 1 and 6, respectively) cells treated with micafungin for 3 h at 37°C.
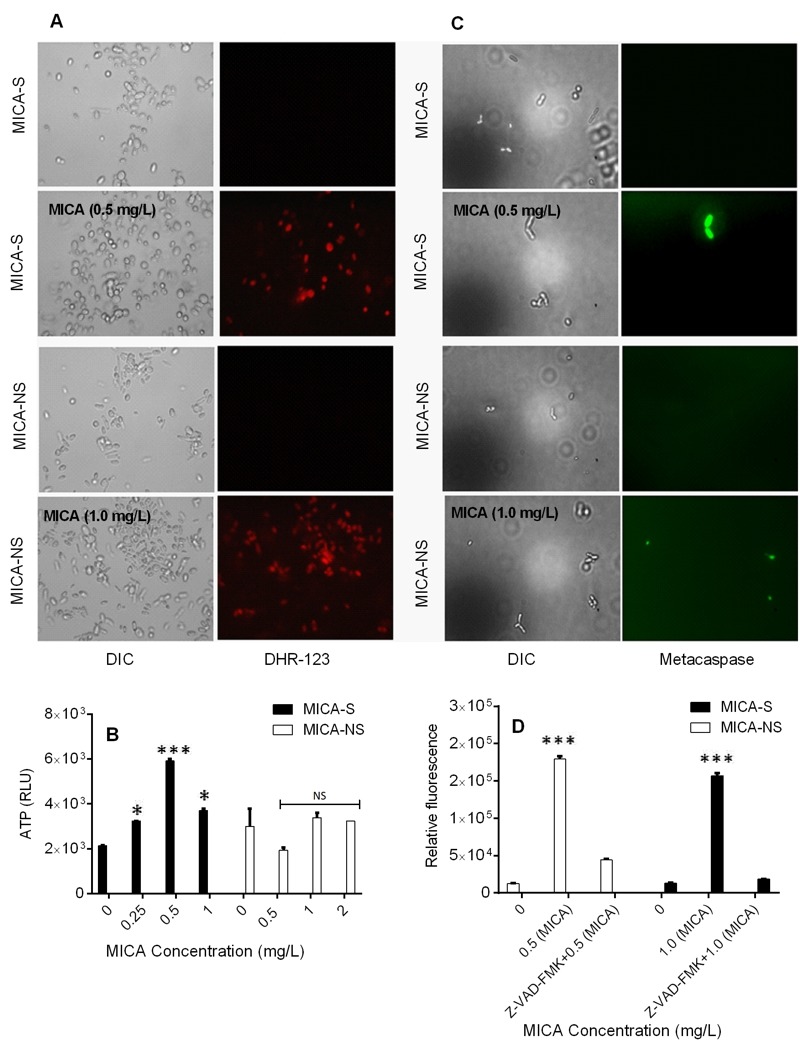
(A) Fluorescence images of MICA-S and MICA-NS strains of C. parapsilosis treated with micafungin and stained for intracellular ROS with DHR-123.
(B) ATP release assay indicating C. parapsilosis cell membrane disruption and plasma membrane leakage after micafungin treatment.
(C) Fluorescent images of MICA-S and MICA-NS C. parapsilosis strains treated with micafungin and stained with caspase activity detection marker CaspACE FITC-VAD-FMK. (D) Relative fluorescence of C. parapsilosis MICA-S and MICA-NS cells treated with micafungin with or without caspase-1 inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK, and stained with caspase activity detection marker CaspACE FITC-VAD-FMK. DIC, Differential Interference Contrast; Cp, C. parapsilosis; RLU, relative light units; *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.0001; NS (non-significant), P > 0.05 (compared with untreated controls).
