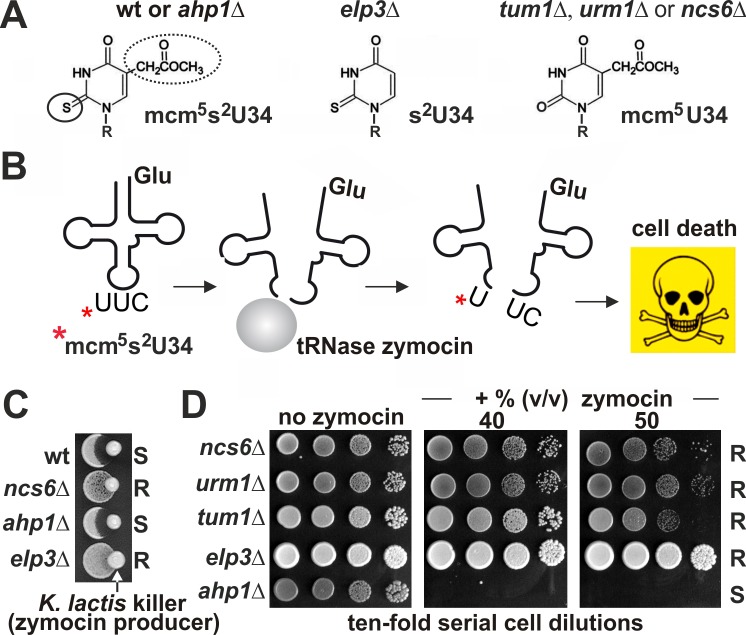
Figure 6. FIGURE 6: The role of Urm1 in tRNA thiolation, not in urmylation of Ahp1, drives tRNase toxicity.
(A) Shown are wobble uridine (U34) modifications from different genetic backgrounds: 5-methoxycarbonyl-methyl-2-thiouridine (mcm5s2U-34), thiouridine (s2U34) and 5-methoxycarbonyl-methyl-uridine (mcm5U34). For simplicity, ‘R’ denotes ribose moieties. U34 thiolation (solid circle) requires S-transfer via Tum1, Urm1•Uba4 and thiolase Ncs2•Ncs6; mcm5 side-chain (dotted circle) formation depends on Elongator 24,28.
(B) The mcm5s2U34 modification (asterisk) in tRNAGluU*UC is efficiently cleaved by zymocin, a fungal tRNase lethal to S. cerevisiae cells (see C) 28,56,57.
(C, D) U34 modification defects (elp3Δ, tum1Δ, urm1Δ, ncs6Δ) protect against zymocin and loss of Ahp1 urmylation (ahp1Δ) confers wild-type (wt) like sensitivity. Growth tests involved killer eclipse assays using K. lactis zymocin producer and the indicated S. cerevisiae tester strains (see C) or toxin plate assays with ten-fold serial dilutions of the indicated tester strains in absence (left panel) or presence (other panels) of different doses of zymocin purified from K. lactis (see D). ‘S’ and ‘R’ indicate toxin sensitive and resistant responses, respectively.