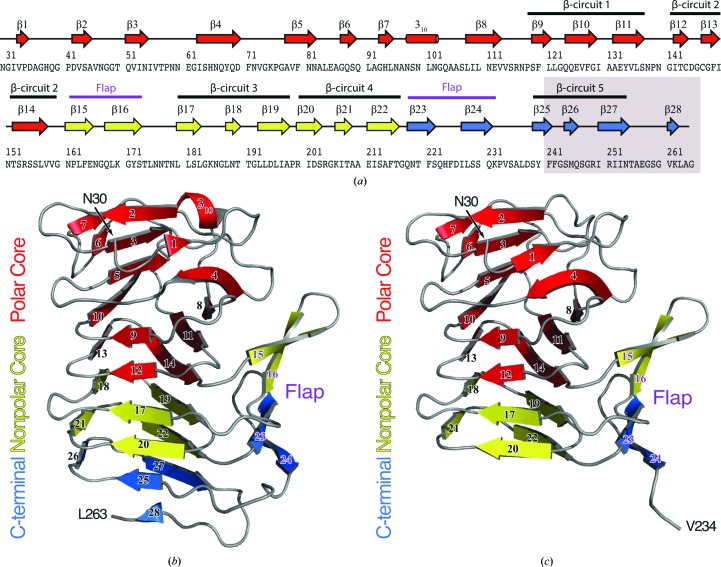
Figure 1.
(a) Secondary-structure diagram of HpmA265. The gray box indicates the region removed by proteolysis in the high-salt structure. The cartoon representations denote the subdomain architecture embedded within (b) the low-salt HpmA265 structure and (c) the high-salt HpmA265 structure. Despite proteolysis in the high-salt structure, both the low-salt and high-salt structures harbor polar core, nonpolar core and carboxy-terminal subdomains. The β-helix core of the HpmA265 structure comprises both the polar and nonpolar core subdomains. Additionally, a four-stranded antiparallel β-sheet (flap) frames one side of the β-helix core. The low-salt crystal form (b) includes residues Asn30–Leu263 and extends through β28 at the C-terminus. The high-salt form (c) includes residues Asn30–Val234 and terminates at β24, which is the final antiparallel β-strand within the flap region.