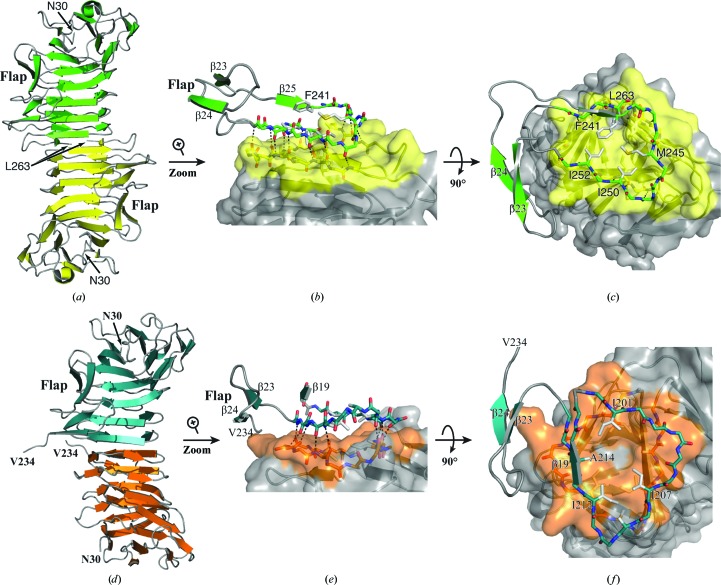
Figure 3.
Dimerization interfaces in the low-salt and high-salt HpmA265 structures. (a) The HpmA265 low-salt crystal structure uses β26–β28 (residues Ser244–Leu263) at the dimerization interface. (b) Magnification of the side view showing hydrogen bonds donated by exposed on-edge β-strands (β26, β27 and β28 residues) from each monomer in the low-salt structure. (c) Top view emphasizing van der Waals interactions during the formation of the low-salt dimer interface. (d) In the AA high-salt crystal structure, proteolysis allows β20–β22 (residues Arg200–Phe215) to establish the dimer interface. (e) Side view emphasizing the hydrogen bonds donated by exposed on-edge β-strands (β20–β22, residues Arg200–Phe215) from each monomer in the high-salt AA structure. (f) A top view showing the van der Waals interactions of Ile201, Ile207, Ile212 and Ala214 during the formation of the high-salt dimer interface.