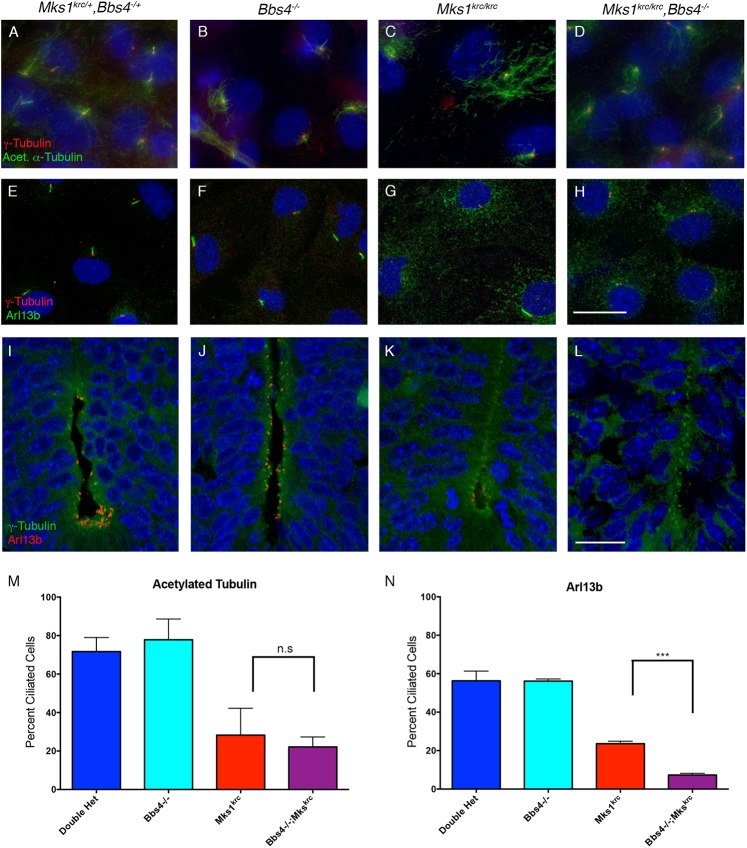
Fig 2. Mks1krc/krc;Bbs4-/- double mutants exhibit enhanced defects in ciliary localization of Arl13b, but not acetylated Tubulin.
(A-H) Mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) were derived from embryos of the indicated genotype, and immunostained for γ-Tubulin (red) and either acetylated α–Tubulin (A-D, green) or ARL13B (E-H, green) to label cilia. Scale bar, 20μm. (I-L) Tissue sections from the embryonic neural tube of double heterozygous (A) Bbs4-/- (B), Mks1krc/krc (C), or Mks1krc/krc;Bbs4-/- double mutant (D) at E10.5. Sections were immunostained for ARL13B to label ciliary membranes (red) and for γ-Tubulin to label centrioles (green). Scale bar, 50μm. (M-N) Quantitation of the percentage of ciliated cells in each genotype positive for either acetylated α-Tubulin (M) or ARL13B (N) following 48 hours of serum starvation. The percentage of cells with cilia stained for acetylated α–Tubulin was not different between double mutants and Mks1krc/krc single mutant cells (M, p = 0.3493). By contrast, significantly fewer double mutant cells had cilia stained with ARL13B compared with Mks1krc/krc single mutant cells (N, *** p = 0.0001).