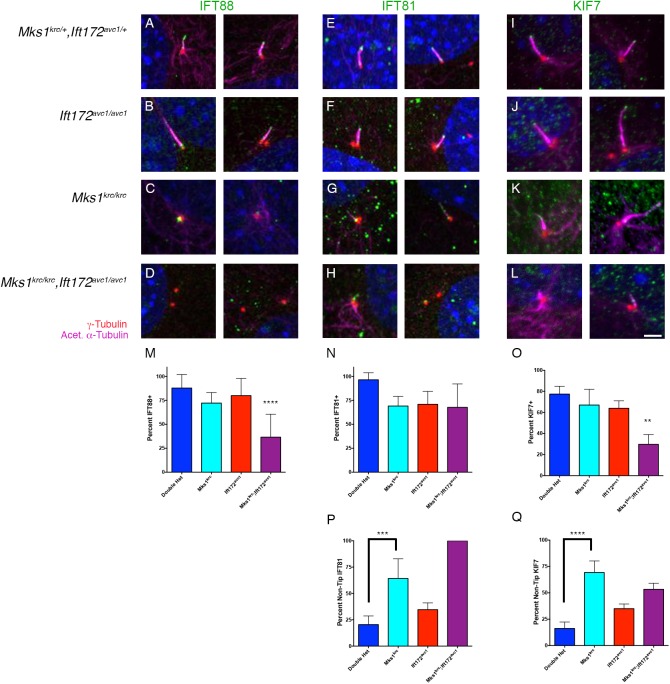
Fig 6. Basal body localization of IFT88 is impaired in Mks1krc/krc;Ift172avc1/avc1 double mutant cells.
(A-L) MEFs derived from embryos of the indicated genotype were immunostained for IFT88 (A-D, green) IFT81 (E-H, green), or KIF7 (I-L, green) together with γ-Tubulin (red) and acetylated α-Tubulin (magenta) following 48 hours of serum starvation. Two representative images for each condition are shown. Scale bar, 2μm. (M-O) Quantitation of the percentage of cells with IFT88 or IFT81 localized to either the basal body or ciliary axoneme. Compared with Mks1krc/krc or Ift172avc1/avc1 single mutant cells, significantly fewer double mutant cilia were positive for IFT88 localized to the basal body (M, **** p< 0.0001). Localization of IFT81 was not significantly disrupted in double mutants compared with either single mutant, however all of the mutants exhibited reduced localization compared with double heterozygous cells (N, p = 0.0015). The percentage of ciliated cells with KIF7 within the axoneme was also significantly reduced in Mks1krc/krc;Ift172avc1/avc1 double mutants compared with single mutant or double heterozygous cells (O, p< 0.001). Quantification for each genotype was based on imaging of 4 separate fields on 3 coverslips per condition. (P-Q) Quantitation of the percentage of cells positive for IFT81 or KIF7 for each genotype in which localization was not restricted to the ciliary tip. Compared with double heterozygous cells, significantly more ciliated Mks1krc/krc cells exhibited localization of IFT81 (p = 0.0005) or KIF7 (p< 0.0001) that was not restricted to the ciliary tip. Quantification for each genotype was based on imaging of 4 separate fields on 3 coverslips per condition.