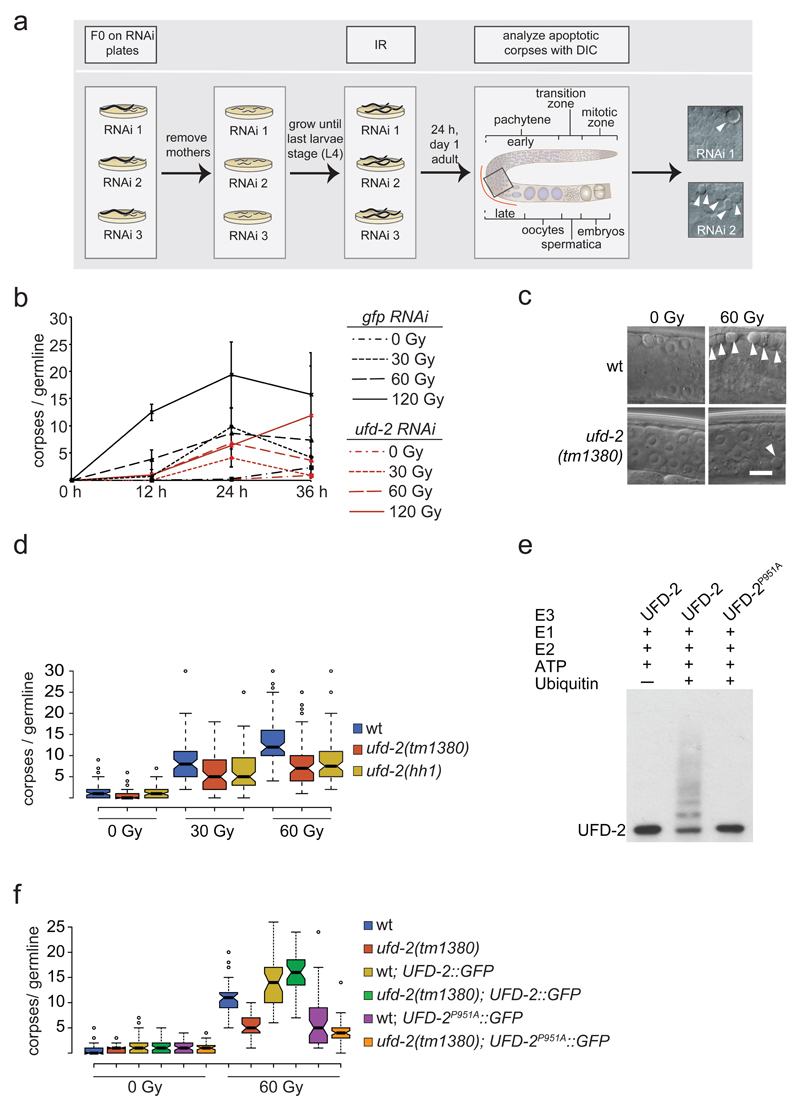
Figure 1.
Ubiquitin ligase activity of UFD-2 is required for apoptosis execution. (a) Schematic illustration of RNAi screen for identification of DNA damage-induced apoptosis mediators. After RNAi treatment worms were subjected to IR and scored for apoptotic corpses (indicated by filled arrowheads) 24 hrs later by differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy. (b) Worms treated with indicated RNAi constructs were exposed to IR of increasing dose and scored for apoptotic corpses 24 hrs after treatment. Data represent mean ± s.e.m. of selected data of RNAi screen. (c) Representative images of late pachytene cells of C. elegans germline 24 hrs after IR treatment. Filled arrowheads indicate an apoptotic corpse. Scale bar 5 µm. (d) Indicated genotypes were scored for DNA damage induced apoptosis 24 hrs after IR. Center lines show the medians; box limits indicate the 25th and 75th percentiles as determined by R software; whiskers extend 1.5 times the interquartile range from the 25th and 75th percentiles, outliers are represented by dots. The notches are defined as +/- 1.58*IQR/sqrt(n) and represent the 95% confidence interval for each median. Non-overlapping notches give roughly 95% confidence that two medians differ. Sample points of 5 independent experiments. (e) Auto-ubiquitylation of UFD-2. Ubiquitylation reactions were carried out as indicated using UFD-2 (wild-type) and UFD-2P951A as ubiquitin ligases. Representative immunoblot of 3 independent experiments. (f) Indicated genotypes were scored for DNA damage induced apoptosis 24 hrs after IR. Sample points of 3 independent experiments. For n-values see Supplementary Table 1.