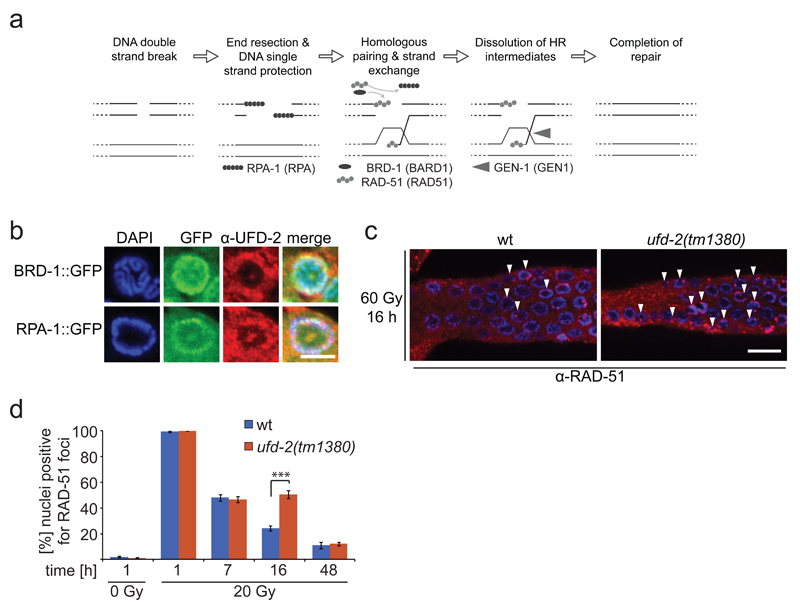
Figure 4.
Loss of ufd-2 delays DSB repair processing. (a) Schematic illustration of DNA DSB repair by HR in C. elegans. Upon DSB induction RPA binds resected single stranded DNA, BRD-1 acts together with BRCA-1 at DSB site, RPA is exchanged for RAD-51, which mediates strand invasion, Gen-1 resolves HJ resulting in repaired DSB. Names in brackets indicate human homologues. (b) Representative images of brd-1::gfp and rpa-1::gfp germlines isolated and stained with α-UFD-2 and DAPI 24 hrs after treatment with 60 Gy of IR. Scale bar, 5 µm. Representative images of 3 independent experiments. (c) Representative images of germlines isolated from wild-type and ufd-2(tm1380) worms 16 hrs after IR treatment with 20 Gy. Germlines were stained with α-RAD-51 and DAPI. Filled arrowheads indicate nuclei positive for RAD-51 staining. Scale bar, 10 µm. (d) Quantification of germ cells that were positive for RAD-51 staining. Wild-type and ufd-2(tm1380) worms were treated with 0 or 20 Gy of IR and isolated 1, 7, 16, 48 hrs after treatment (7, 16, 48 hrs only for 60 Gy treated worms) and immunostained with α-RAD-51 and DAPI to stain DNA. The last 50 nuclei of pachytene germ cells prior entering diakinesis were evaluated. Data show means ± s.e.m. of 3 independent experiments. The triple asterisk indicates P value of ≤ 0.001 in Student’s t-test. For n-values see Supplementary Table 1.