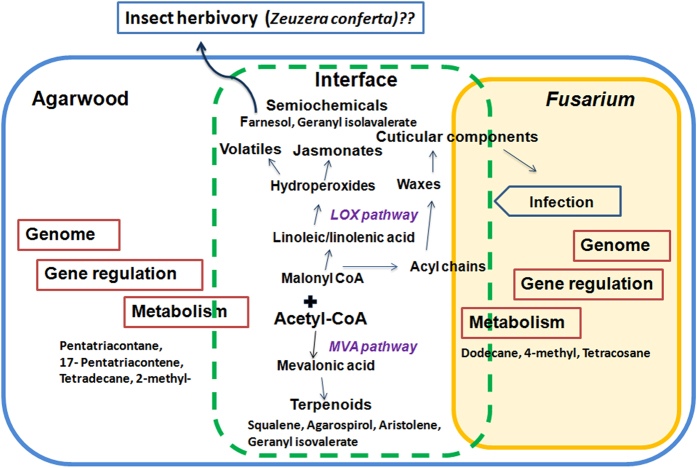
Figure 7. Fragrant agarwood as an outcome of fungus-plant interactions.
The layout of plant–pathogen interaction given in Pinney (2011)43 was adopted to summarize the findings. The complex regulation of the genetic and metabolic machineries of agarwood and Fusarium at the interface led to modulation of defense, secondary metabolism related pathways (LOX, jasmonate, waxes, MVA) and metabolites. The comparison of metabolic phenotypes by GC-MS based profiling and correlation network analysis, revealed change in levels of terpenoids, waxes, volatiles, semiochemicals and other key metabolites (agarwood sesquiterpenes) that bear chemometric signatures of fragrant agarwood production.