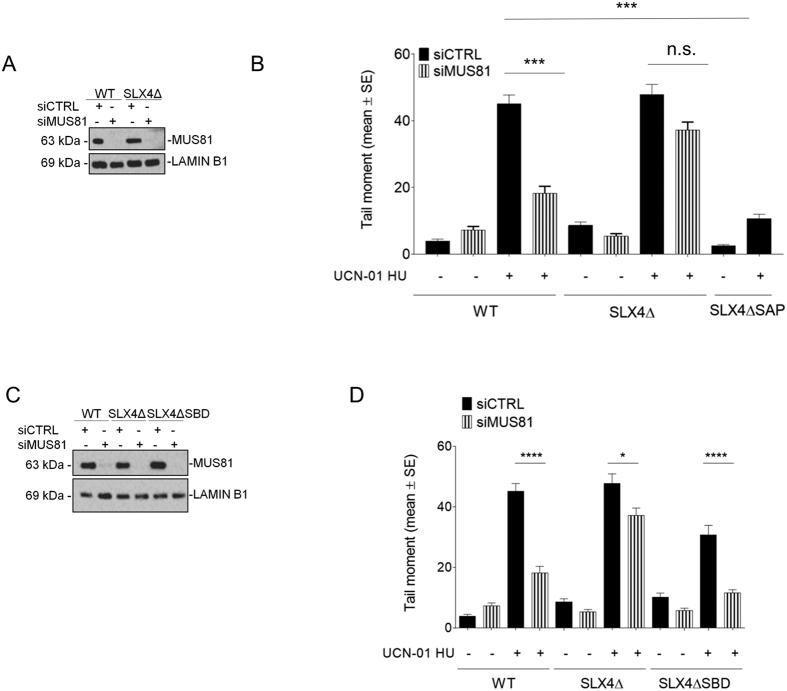
Figure 3. Abrogation of the SLX4-MUS81 or SLX4-SLX1 interaction does not stimulate GEN1-dependent DSBs formation.
(A) Western immunoblotting showing MUS81 depletion in SLX4-deficient FA-P cells (SLX4Δ), complemented with wild-type SLX4 (WT). Lysates were prepared 48 h after transfection with indicated siRNA oligos. LAMIN B1 was used as a loading control. (B) SLX4-deficient FA-P cells (SLX4Δ), complemented with wild-type SLX4 (WT) or with the deletion mutant that abrogate MUS81 interaction (SLX4ΔSAP) were transfected with control siRNA (siCTRL) or siRNAs against MUS81 (siMUS81). The amount of DSBs was evaluated by neutral Comet assay after depletion of MUS81 and treatment with 600 nM UCN-01 and 2 mM HU for 6 h. Graph shows the mean tail moment +/− SE from three independent experiments. (ns = not significant p > 0.05; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, Kruskal-Wallis test). (C) Western immunoblotting showing MUS81 depletion in SLX4-deficient FA-P cells (SLX4Δ), complemented with wild-type SLX4 (WT) or the SLX4 deletion mutant abrogating interaction with SLX1 (SLX4ΔSBD). Lysates were prepared 48 h after transfection with indicated siRNA oligos. LAMIN B1 was used as a loading control. (D) SLX4-deficient FA-P cells (SLX4Δ), complemented with wild-type SLX4 (WT) or with the deletion mutant that abrogates SLX1/SLX4 interaction (SLX4ΔSBD) were transfected with control siRNA (siCTRL) or siRNAs against MUS81 (siMUS81). The amount of DSBs was evaluated by neutral Comet assay after treatment with 600 nM UCN-01 and 2 mM HU for 6 h. Graph shows the mean tail moment +/− SE from three independent experiments. (ns = not significant p > 0.05; *p < 0.05; ****p < 0.0001, Kruskal-Wallis test). Uncropped versions of gels are provided in Supplementary Material.