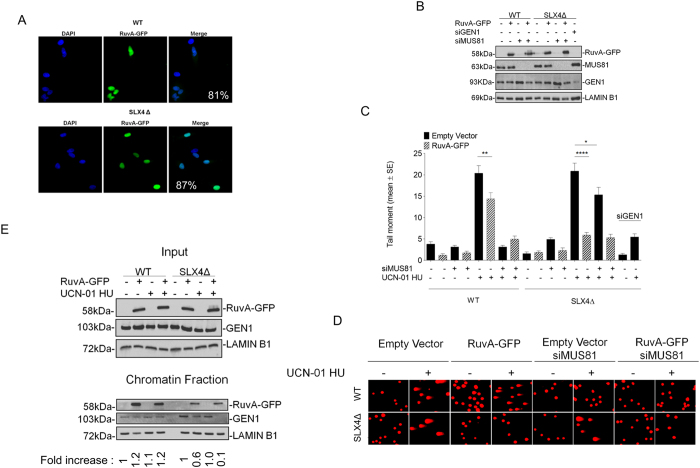
Figure 4. RuvA-GFP expression abrogates GEN1-dependent DSBs in SLX4-deficient FA-P cells.
(A) Expression of RuvA-GFP tagged protein in SLX4-deficient FA-P cells (SLX4Δ), complemented or not with wild-type SLX4 (WT). Seventy-two hours after transfection, cells were fixed and nuclei were stained with DAPI. Representative microscopy fields are presented. The percentage of RuvA-positive cells in the population is reported in the merged images. (B) Western immunoblotting showing RuvA-GFP expression, MUS81 or GEN1 depletion in SLX4-deficient FA-P cells (SLX4Δ), and in cells complemented with wild-type SLX4 (WT). Lysates were prepared 48 h after transfection with indicated plasmid or siRNA oligos. LAMIN B1 was used as a loading control. (C) Analysis of DSBs by neutral Comet assay. SLX4-deficient FA-P cells, complemented or not with wild type SLX4, were transfected with RuvA-GFP in combination or not with siRNAs directed against MUS81 (siMUS81) or GEN1 (siGEN1), as indicated. Seventy-two hours after transfections, cells treated for 6 h with 600 nM UCN-01 and 2 mM HU. Graph shows the results from three independent experiments. Data are presented as mean +/− SE. (ns = not significant p > 0.05; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.001, Kruskal-Wallis test). Representative images of comets are presented in (D). (E) Analysis of GEN1 recruitment in chromatin after replication stress. FA-P cells complemented or not with wild type SLX4 were transfected with RuvA-GFP DNA and GEN1 recruitment in chromatin was evaluated after 6 h of treatments with 600 nM UCN-01 and 2 mM HU by cellular fractionation and Western blotting with indicated antibodies. Before cellular fractionation, an aliquot (10%) of cell suspension was used to assess that amount of GEN1 in all samples (Input). LAMIN B1 was used as a loading control. The fold increase value indicating the amount of GEN1 in chromatin compared to untreated condition is reported below the blot. Uncropped versions of gels are provided in Supplementary Material.