Figure 8. A model depicting the impact of HSCs on NK cell anti-fibrotic functions in LC patients with HBV infection.
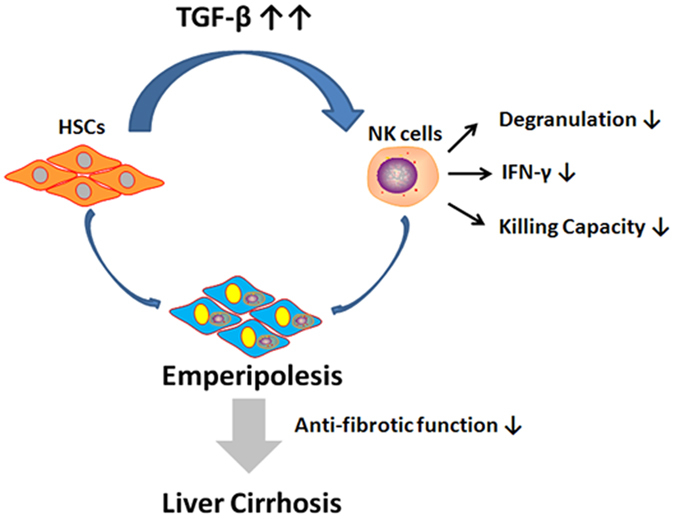
In advanced liver fibrosis, activated HSCs generally produce a large amount of TGF-β that might suppress NK cell anti-fibrotic functions, such as degranulation, IFN-γ production and killing activity against HSCs. The HSCs might then internalize these functionally impaired NK cells in an emperipolesis-dependent manner, thus promoting the progression of liver fibrosis.
