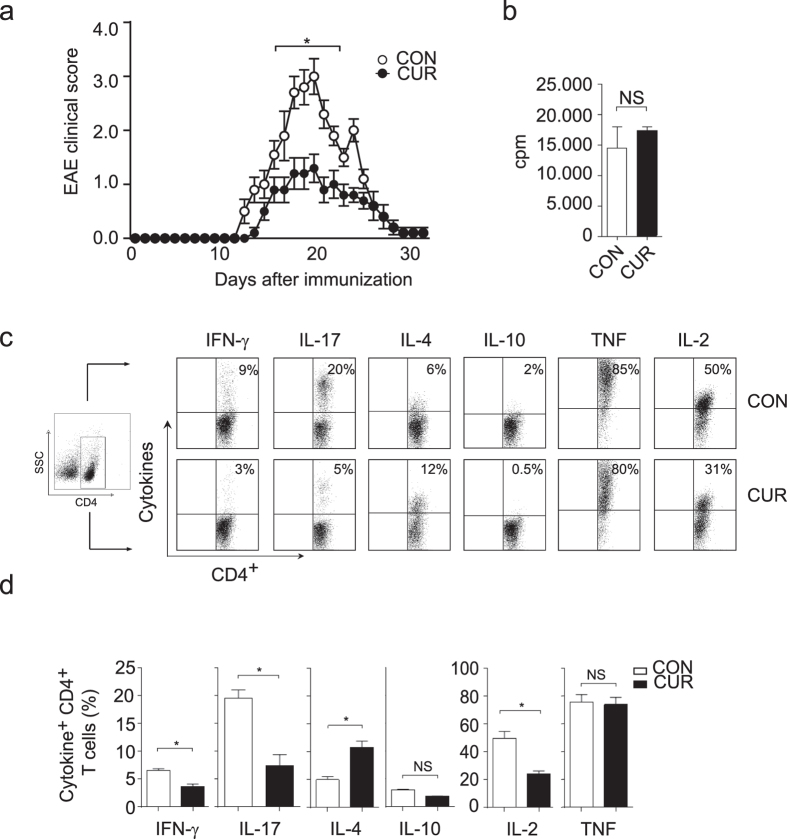
Figure 1. CUR protects mice from severe encephalomyelitis and inhibits IL-17 and IFN-γ production in vivo.
(a) Mice were fed with 2% CUR or control diet (CON), immunized for EAE and followed for disease symptoms. The results show mean EAE score ± SEM from 2 independent experiments with n = 16 mice (*P < 0.05 day 16 to 22; Wilcoxon test). (b) Mice were fed with CUR as in (a) and immunized for EAE. On day 7 after immunization, CD4+ T cells were purified from draining lymph nodes and co-cultured with DC and PLP peptide. T cell proliferation was assessed by [3H] thymidine incorporation. NS: not significant, Mann-Whitney test. (c,d) Mice were treated as in (a). On day seven after immunization draining lymph nodes were isolated to analyze intracellular cytokine production in PMA/ionomycin-stimulated CD4+ T cells. First, a FSC/SSC plot was made and all lymph node cells were gated. The CD4+ T cell population was gated by a SSC/CD4 (left panel) plot and then analyzed for CD4+ T cell-specific cytokine expression. Dot plots from single mice are depicted in (c), pooled data from control mice (CON; n = 5) and CUR-treated mice (CUR; n = 5) are shown in (d). Bars represent the mean ± SEM (*P < 0.05, Mann-Whitney test).