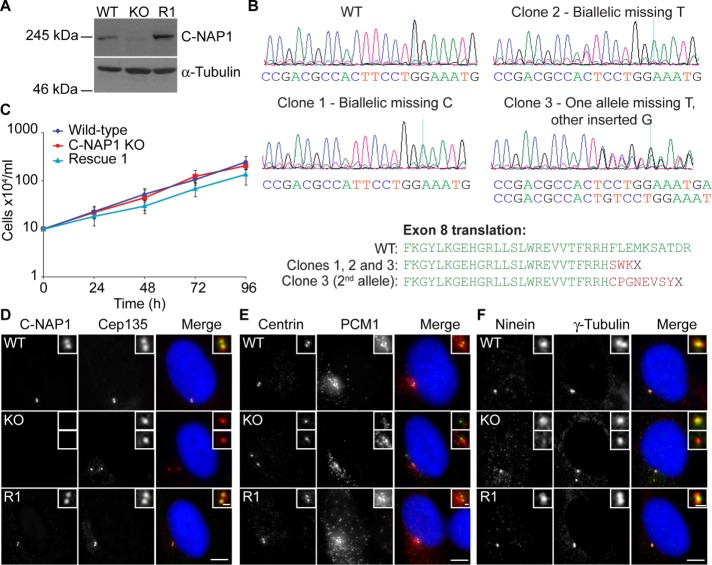
FIGURE 1:
Generation of C-NAP1 null hTERT-RPE1 cells and preliminary phenotypic analysis. (A) Immunoblot of wild-type, C-NAP1–knockout (KO) clone 1, and C-NAP1 rescue (R1) cells using anti–C-NAP1 monoclonal 6F2C8. α-Tubulin was used as a loading control. (B) Sequence analysis of C-NAP1–deficient clones. PCR was performed on genomic DNA from the candidate clones and both total (shown in the traces) and cloned, individual PCR products were cloned and sequenced (five per clone). All sequences for clones 1 and 2 were identical. In sequencing clone 3 products, deletion of a thymine occurred in three of the five samples, with incorporation of a guanine in the other two. (C) Proliferative analysis of cells of the indicated C-NAP1 genotype. We plated 2 × 105 cells in 2 ml at 0 h and at 24, 48, 72, and 96 h. The cells were counted and the culture split 1:2. Data points show mean ± SD of three independent experiments. No significant difference was observed between wild type (WT) and C-NAP1 nulls at any time point. (D–F) Immunofluorescence microscopy of the indicated centrosomal markers in cells of the indicated C-NAP1 genotype. Scale bar, 5 μm.