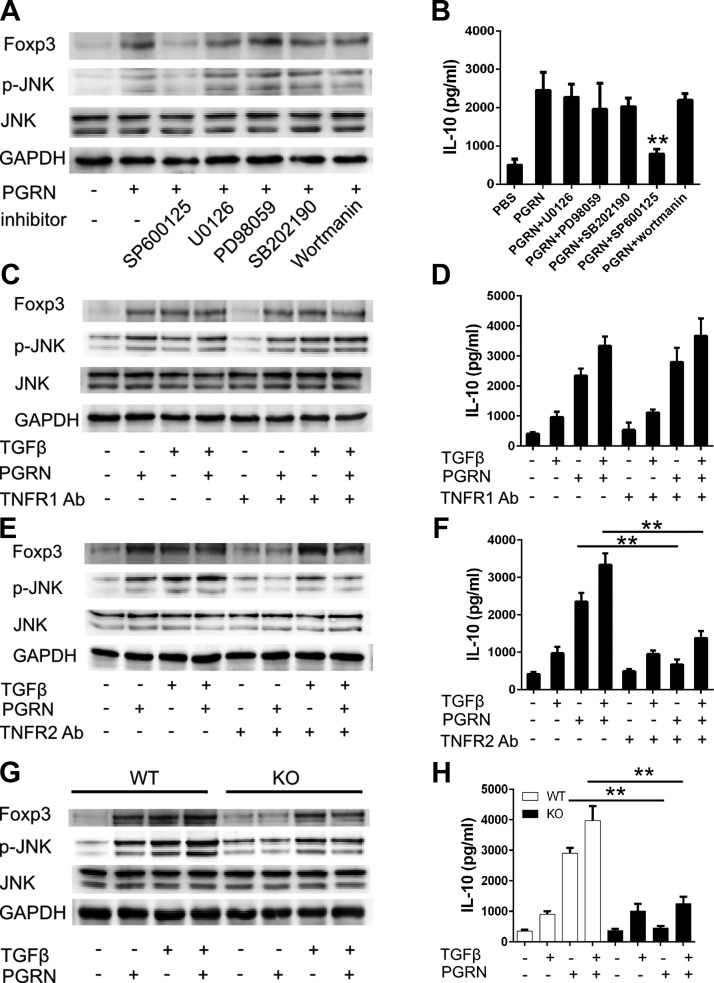
Figure 5.
PGRN-stimulated expression of Foxp3 and IL-10 depend on TNFR2/JNK pathway. A, B) CD4+ T cells that were isolated from WT mice were treated with indicated inhibitors for 1 h before incubation with PGRN. Cells were isolated after 4 d to determine expression of FoxP3 or 4 h to determine the phosphorylation of JNK by immuoblotting (A), and IL-10 in 4-d culture supernatant was determined by ELISA (B). C, D) Isolated CD4+ T cells were pretreated with or without TNFR1 Abs for 1 h. Cells were then cultured with PGRN in the presence or absence of TGF-β. Cells were isolated after 4 d to determine expression of Foxp3 or 4 h to determine the phosphorylation of JNK by immuoblotting (C), and IL-10 in 4-d culture supernatant was determined by ELISA (D). E, F) Isolated CD4+ T cells were pretreated with or without TNFR2 Abs for 1 h. Cells were then cultured with PGRN in the presence or absence of TGF-β. Cells were isolated after 4 d to determine expression of Foxp3 or 4 h to determine the phosphorylation of JNK by immuoblotting (E), and IL-10 in 4-d culture supernatant was determined by ELISA (F). G, H) CD4+ T cells were isolated from WT or TNFR2−/− mice. Isolated cells were incubated with PGRN in the presence or absence of TGF-β. Cells were isolated after 4 d to determine expression of FoxP3 or 4 h to determine the phosphorylation of JNK by immuoblotting (G), and IL-10 in 4-d culture supernatant was determined by ELISA (H). GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; KO, knockout. Results are means ± sd from 3 independent experiments. **P < 0.01 vs. control group.