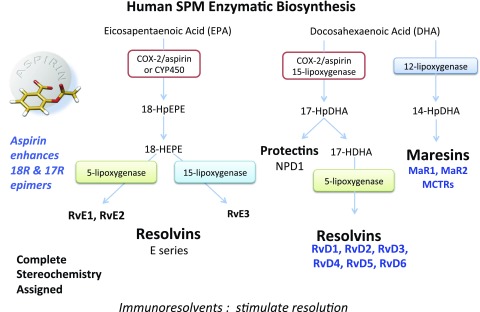
Figure 2.
Human SPM biosynthetic routes. Biosynthesis of E-series Rvs is initiated with molecular oxygen insertion at carbon-18 position of EPA, which is converted to bioactive E-series members RvE1–E3. The resolution metabolome also activates 17-lipoxygenation of DHA; 17S-HpDHA is converted to Rv-epoxide intermediates by the leukocyte 5-LOX. The intermediates are transformed to RvD1–D6, each of which carries potent actions. 17-HpDHA is also the precursor to the 16,17-epoxide-PD intermediate, which is converted to NPD1/PD1 and related PDs (see Fig. 6A). MaRs are produced by macrophages via initial lipoxygenation at the carbon-14 position by lipoxygenation and insertion of molecular oxygen, producing a 13S,14S-epoxide-MaR intermediate that is enzymatically converted to the MaR family members MaR1, MaR2, and MCTRs. The stereochemistry of each bioactive SPM has been established, and SPM biosynthesis in murine exudates and human tissues confirmed. (See refs. 58, 103, 163, 164 for original reports, total organic synthesis, and stereochemical assignments and the text for further details. For complete stereochemistry of individual SPMs, see refs. 72, 104, 107.) Low-dose aspirin triggers the 17R and 18R/S epimers of the Rvs (9, 53) and 17R-epimer PDs (165, 166).