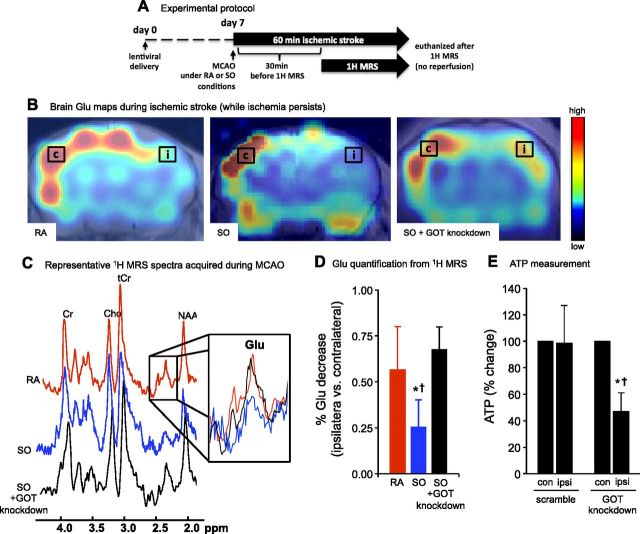
Figure 2.
GOT enables reduction of cortical Glu in stroke-affected brain. A) Experimental protocol. B) 1H MRS chemical shift images were acquired 30 min after the onset of MCAO under RA, SO, or SO + GOT-knockdown conditions. Spectra were acquired from contralateral (c) and stroke-affected ispsilateral (i) regions in the S1 cortex. C) Representative RA (red), SO (blue), and SO + GOT-knockdown (black) spectra from voxel in ipsilateral cortex. Zoomed inset depicts Glu peaks under each condition. D) Percentage Glu decrease in ipsilateral cortex compared with contralateral cortex under RA (red bar), SO (blue bar), and SO + GOT knockdown (black bar) conditions. Data are means ± sd (n = 6). *P < 0.05 vs. RA. †P < 0.05 vs. SO + GOT knockdown. E) Percentage change in brain ATP (ipsilateral vs. contralateral) from GOT-knockdown and scramble control mice under SO conditions after 30 min of MCAO. Data are means ± sd (n = 6). *P < 0.05 vs. contralateral (con) hemisphere within group. †P < 0.05 vs. ipsilateral (ipsi) scramble.