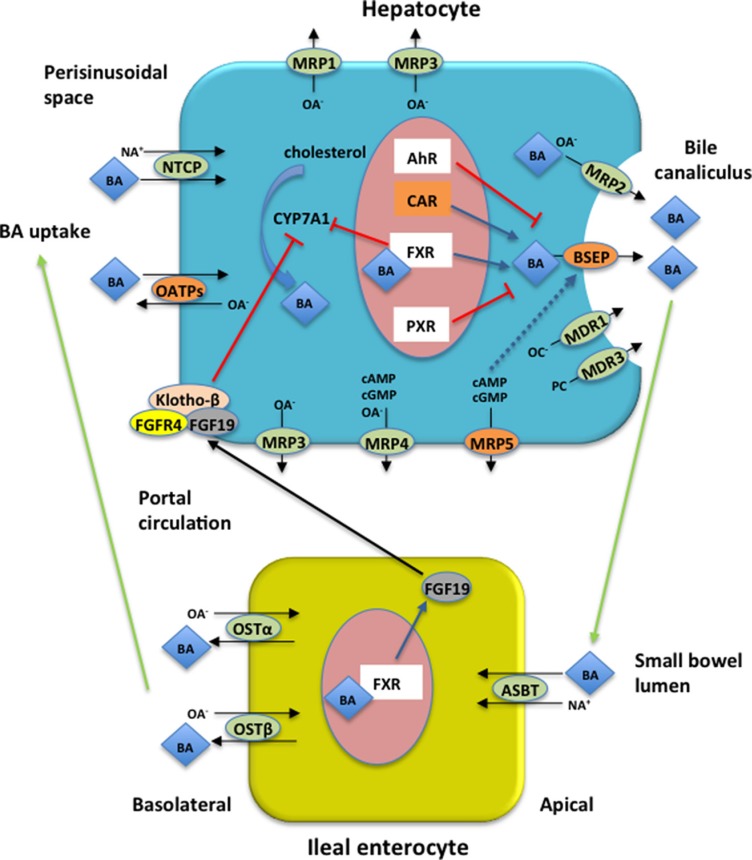
Figure 2. Enterohepatic circulation (EC) of bile acids (BAs) and proteins encoded by the four genes associated with GIS in FD patients.
Major BA transporters in human hepatocytes and enterocytes are shown. Blue arrows indicate up-regulation, red bars indicate down-regulation, while black arrows indicate transport across the cell. Proteins encoded by the four genes reported in the current study associated with GIS are represented in orange boxes. BAs are synthesized in hepatocytes from cholesterol by CYP7A1 which is thought to be the rate limiting step in BA synthesis. BAs active FXR to inhibit CYP7A1 gene transcription. FXR induces intestinal hormone FGF19 which is released in the portal circulation and in the hepatocytes activates FGFR4/Klotho-β signaling inhibiting CYP7A1 activity. In hepatocytes BSEP excretes monovalent BAs in the bile canaliculus while divalent BAs and anionic conjugates are excreted via MRP2. MDR3 mediates secretion of phopholipids while organic cations are excreted via MDR1. Basolateral bile acid export system (MRP1, MRP3, MRP4, MRP5) excretes accumulated biliary constituents. In the terminal ilieum BAs are reabsorbed by ASBT and effluxed on the basolateral site via OSTα/β. BAs are taken up by the hepatocytes via NTCP and OATPs transport systems. BSEP expression is regulated by nuclear receptors (see text for details) and BSEP insertion into canalicular membrane is stimulated by cAMP (blue dashed arrow). AhR = aryl hydrocarbon receptor; ASBT = apical sodium bile salt transporter; BA = bile acid; BSEP = bile salt expert pump; CAR = constitutive androstane receptor; CYP7A1 = cholesterol 7a-hydroxylase; FGF19 = fibroblast growth factor 19; FGFR4 = FGF receptor 4; FXR = farsenoid X receptor; MRP1= multidrug resistance protein 1; MRP2 = multidrug resistance protein 2; MRP3= multidrug resistance protein 3; MRP4 = multidrug resistance protein 4; MRP5 = multidrug resistance protein 5; NA+ = sodium ion; NTCP = Na+-dependent taurocholate cotransport peptide; OATPs = Na+-independent organic anion transport proteins; OA- = organic anions; OC- = organic cations; OSTα/β = organic solute transporter α/β; PC = phosphatidylcholine; PXR = pregnance X receptor.