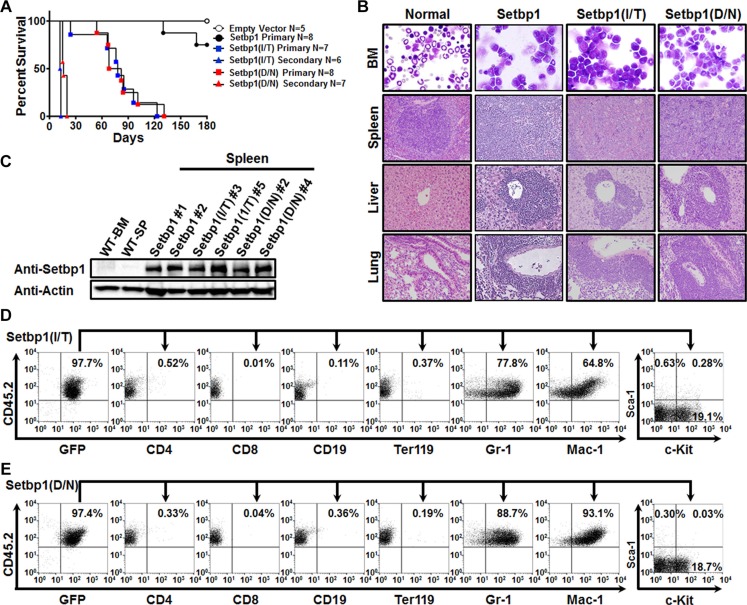
Figure 2. Setbp1 missense mutations induces AML development.
(A) Survival curves of lethally-irradiated C57BL6-Ly5.2 mice receiving 5-FU treated bone marrow progenitors transduced with pMYs-IRES-GFP, pMYs-Setbp1-IRES-GFP, pMYs-Setbp1(I/T)-IRES-GFP, or pMYs-Setbp1(D/N)-IRES-GFP virus, or 1 × 106 spleen cells from primary leukemic mice. (B) Representative cytospin analysis of bone marrow (BM) cells from leukemic mice and H&E staining of spleen, liver, and lung tissue sections showing leukemic infiltration in Setbp1 mutants-induced leukemic mice. (C) Western blotting analysis of Setbp1 and β-Actin in wild-type bone marrow (WT-BM) and spleen (WT-SP), and leukemic spleens induced by wild-type or mutant Setbp1. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 (two-tailed Student’s t test). (D) Representative FACS analysis of GFP and CD45.2 double positive leukemia cells from the bone marrow of Setbp1(I/T)-induced leukemic mice using the indicated antibodies. Numbers represent the percentages of gated events. (E) Representative FACS analysis of GFP and CD45.2 double positive leukemia cells from the bone marrow of Setbp1(D/N)-induced leukemic mice using the indicated antibodies. Numbers represent the percentages of gated events.