Figure 2. Binding of 4LB5-HP-RNase to NCL on cancer cells.
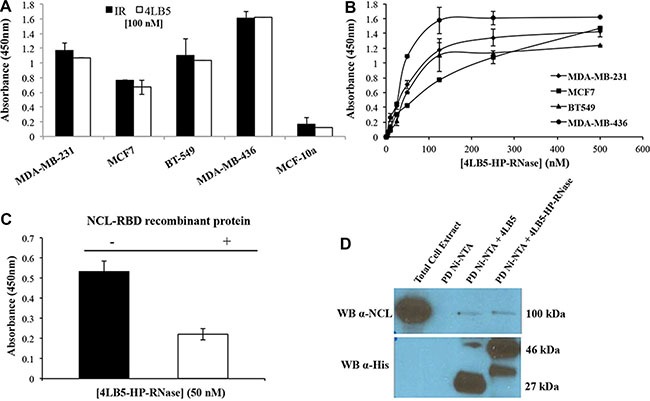
(A) The binding of 4LB5-HP-RNase to NCL-positive MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, BT-549 or MDA-MB-436 breast cancer cells or to NCL-negative MCF-10a normal-like breast cells was tested by incubating the chimeric protein (100 nM) with the cells; 4LB5 was tested at equimolar doses as a positive control in parallel assays. (B) Binding curves of 4LB5-HP-RNase to surface NCL-positive MDA-MB-231 (rhomboids), MCF-7 (squares), BT-549 (triangles), MDA-MB-436 (circles) breast cancer cell lines performed by using increasing concentrations (5–500 nM) of the immunoRNase. All the experiments are representative of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Mean + SD is reported. (C) ELISA assay performed by testing 4LB5-HP-RNase (50 nM) on MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells in the absence (black) or in the presence (white) of equimolar doses of NCL-RBD recombinant protein. All the experiments are representative of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Mean + SD is reported. (D) Pull-down assay performed on lysates of MDA-MB-231 cells using Ni-NTA resin and 4LB5 or 4LB5-HP-RNase. Ni-NTA resin incubated with total cell lysate in the absence of 4LB5 or 4LB5-HP-RNase was used as negative control. Anti-NCL antibody (upper panel) and anti-His antibody (Lower panel) were used to visualize the effective pull-down of endogenous NCL in the presence of either 4LB5 or 4LB5-HP-RNase.
