Fig. 1.
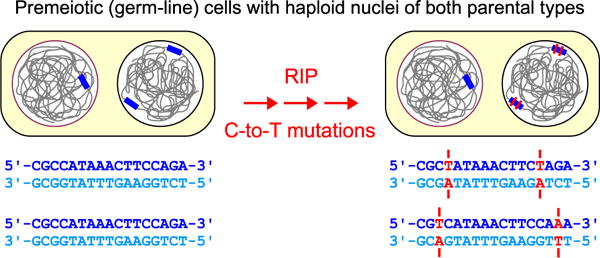
Phenomenon of repeat-induced point mutation (RIP). RIP can detect homology between DNA sequences exhibiting a wide range of particular base-pair compositions, transcriptional capacities, and relative as well as absolute positions in the genome (Galagan and Selker 2004). Both sequence copies undergo mutation by numerous C-to-T transitions specifically over the extent of shared homology. RIP occurs during the premeiotic stage, after fertilization but before karyogamy, in parental haploid nuclei that continue to divide by mitosis
