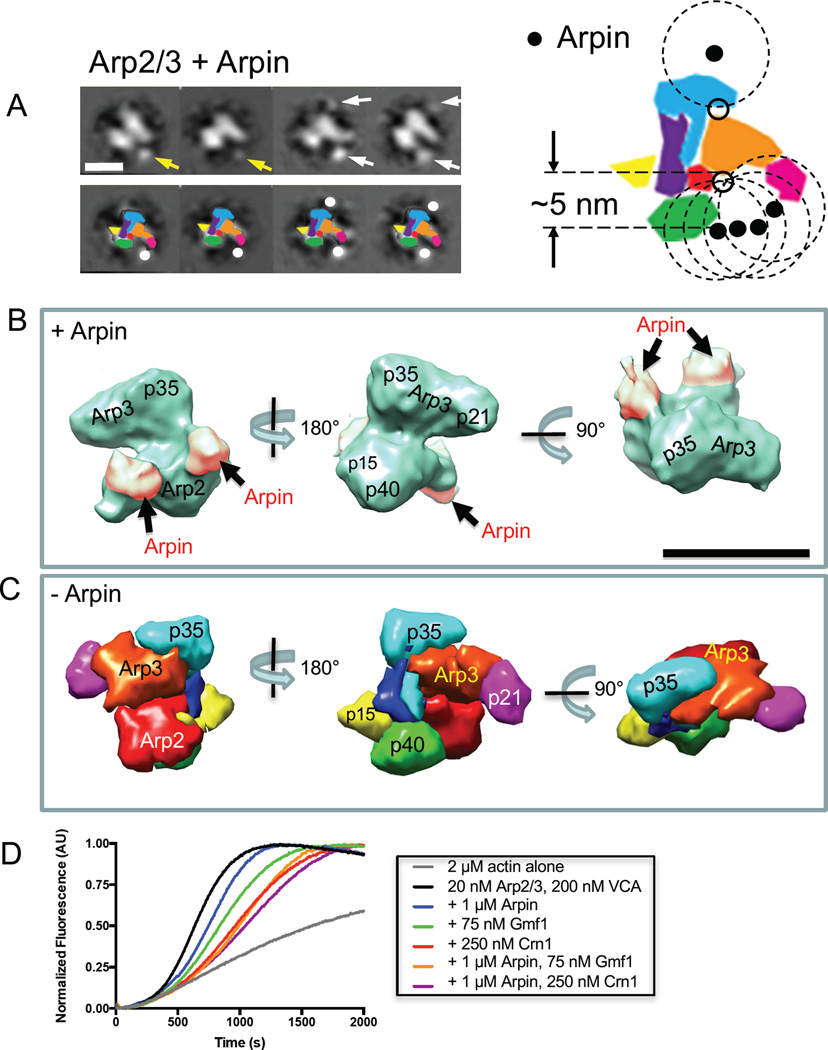
Figure 4. Three-dimensional structure of Arpin-bound Arp2/3 complex.
(A) Two-dimensional projections of Arpin-bound Arp2/3 complex. Arrows highlight new masses, which likely represent the globular core domains of Arpin [40]. Yellow arrows indicate the presence of a single new mass, while white arrows indicate two new masses. Scale bar, 10 nm. Lower panel includes corresponding cartoons of each class average. The larger cartoon on the right shows Arp2/3 complex with superimposed positions of Arpin (filled circles). Dashed circles have a 5 nm radius, corresponding to the estimated length connecting the center of Arpin globular domain and its C-terminal acidic (A) motif. The circles were used to map potential Arpin-binding sites on Arp2/3 complex (open circles). (B) Three-dimensional reconstruction of Arpin-bound Arp2/3 complex viewed from different angles. Additional density, attributed to Arpin, is shaded pink. (C) Crystal structure of Arp2/3 complex [14] filtered to 25 Å resolution using UCSF Chimera [51], with subunits color-coded and labeled. Views are aligned with those in B for comparison. Scale bar, 10 nm. (D) Bulk actin polymerization assays containing G-actin (2 µM, 5% pyrene-labeled) and the indicated concentrations of Arp2/3 complex, VCA, Arpin, Gmf1, and Crn1.