FIGURE 7.
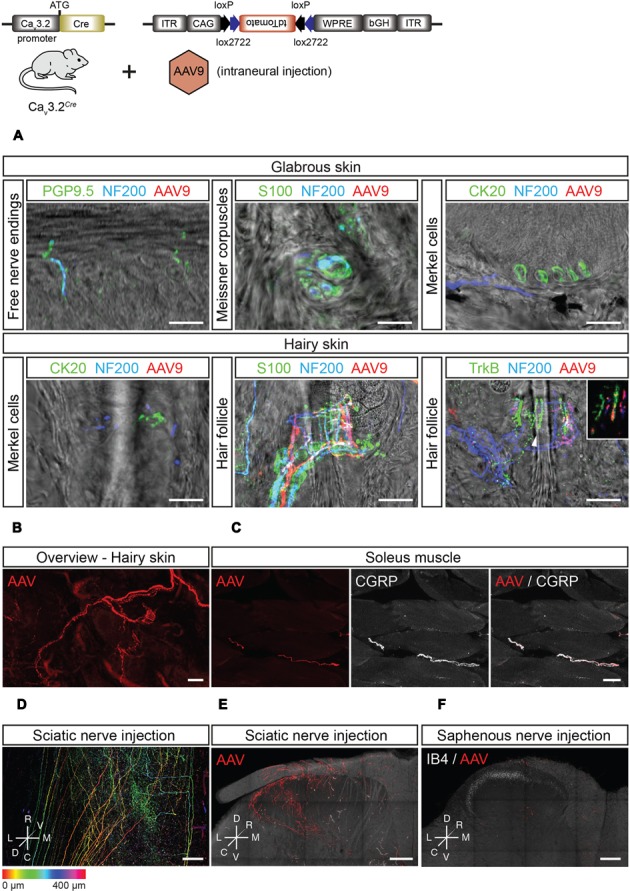
Peripheral and central innervation of tdTomato positive cells of virally transduced Cav3.2Cre mice. (A) Sensory end organs in the skin and their innervation by sensory afferents in virally transduced Cav3.2Cre mice after intrasciatic AAV injection. Sensory fibers were labeled using NF200 and/or PGP9.5. In the glabrous skin, Meissner corpuscles were visualized using an antibody against S100, and Merkel cells were stained using an antibody against CK20. In the hairy skin, Merkel cells were also immunostained using an antibody against CK20. Hair follicles were visualized by immunostaining of terminal Schwann cells using an antibody against S100. Hair follicle afferents were immunostained with antibodies against NF200 and TrkB. Scale bars: 20 μm. (B) Whole-mount imaging of hairy skin with tdTomato+ fibers innervating hair follicles. Scale bar: 25 μm. (C) In the soleus muscle, tdTomato+ sensory afferents were observed and identified as nociceptors by immunostaining using an antibody against CGRP. Scale bar: 20 μm. (D–F) Central termination of virally transduced Cav3.2Cre positive fibers after intrasciatic AAV injection. (D) Dorsoventral projection (with depth color coding) of a tiled image stack of the lumbar spinal cord of a Cav3.2Cre mouse showing TdTomato+ central terminals of Cav3.2Cre expressing sensory neurons, Scale bar: 100 μm. (E) Maximum intensity projections of a thick transverse slice of the lumbar spinal cord after intra-sciatic nerve AAV injection. Scale bar: 100 μm. (F) Maximum intensity projection of a thick transverse slice of the lumbar spinal cord after intra-saphenous nerve AAV injection. Scale bar: 100 μm.
