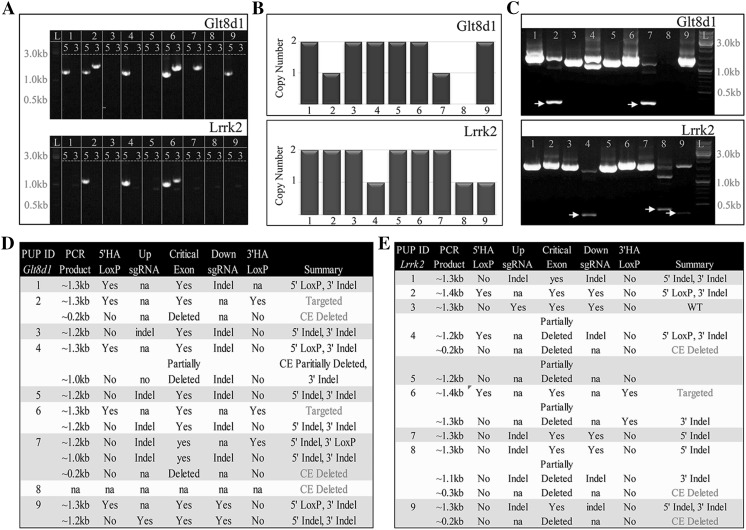
Fig. 4.
CRISPR/Cas9 induces efficient multi-vector targeting via HDR and NHEJ mediated gene knockout via a single injection to mouse zygotes. a Junction PCR at 5′ and 3′ homology arms to verify targeting of pKOMP-Glt8d1 and pKOMP-Lrrk2 in the nine founder pups. b RT-qPCR to evaluate copy number of Glt8d1 and Lrrk2 critical exons in the nine founder pups. c PCR to determine critical exon deletion due to sgRNAs targeting regions flanking the critical exons of Glt8d1 or Lrrk2 in the nine founder pups. Yellow arrows, amplicons resulting from critical exon deletions. d, e Summary of sequencing data derived from the gel-extracted PCR products from (c). First columns, ID of pups for Glt8d1 and Lrrk2; second columns, approximate size of the PCR products that were gel extracted from (c); third columns, indicate presence of 5′HA loxP sequences; fourth columns, indicate presence of indels in the Upstream-sgRNA target regions—not applicable (na), indicates presence of 5′HA LoxP; fifth columns indicate it the critical exons are present, deleted, or partially deleted; sixth columns, show presence of indels in the Downstream-sgRNA target regions—not applicable (na) indicates presence of 3′HA LoxP; seventh columns indicates presence of 3′HA loxP sequences; last column, summary of sequence data. Red letters indicate targeted or critical exon (CE)—deleted alleles. (Color figure online)