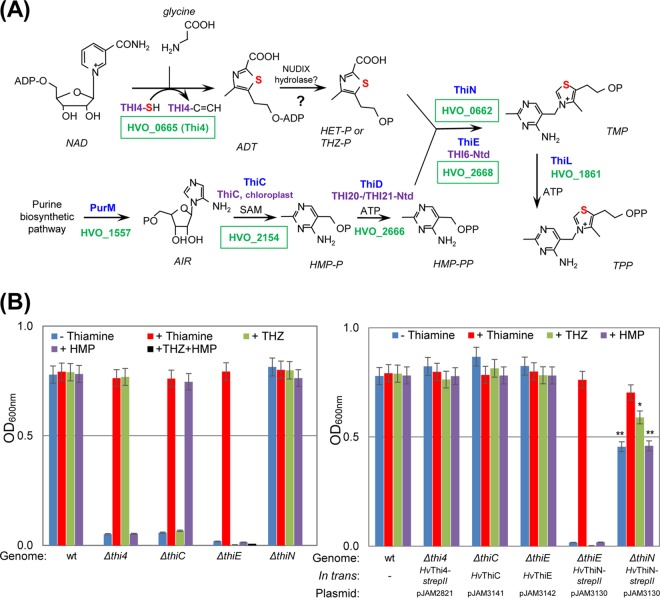
FIG 1.
De novo pathway of thiamine biosynthesis in H. volcanii and growth assay. (A) Thiamine biosynthesis in H. volcanii is a hybrid of bacterium-like pyrimidine (bottom) and eukaryote-like thiazole (top) synthesis pathways. The sulfur atom associated with the formation of the thiazole ring is highlighted in red. Thiamine-biosynthetic enzymes of bacteria, yeast, and H. volcanii are indicated in blue, purple, and green, respectively. Homologs of H. volcanii characterized in this study are shown in green boxes. (B) The single-gene deletion mutants and trans-complemented strains were grown in minimal medium (GMM) without (−) or supplemented with (+) thiamine, THZ, and/or HMP, where strepII indicates a C-terminal Strep-tag II fusion. Growth was monitored as the OD600. Data represent mean results ± standard errors of the means from three independent experiments (n = 3). P values were determined by two-tailed, unpaired Student's t test (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01). See Materials and Methods for details. Abbreviations: ADT, ADP-thiazole; THZ-P or HET-P, 4-methyl-5-(β-hydroxyethyl)thiazole phosphate; AIR, 5-aminoimidazole ribotide; SAM, S-adenosyl-methionine; HMP-P, 4-aminohydroxymethyl-2-methylpyrimidine phosphate; HMP-PP, 4-aminohydroxymethyl-2-methylpyrimidine pyrophosphate; TMP, thiamine monophosphate; TPP, thiamine pyrophosphate.